A recently patched security flaw impacting VMware ESXi hypervisors has been actively exploited by “several” ransomware groups to gain elevated permissions and deploy file-encrypting malware.
The attacks involve the exploitation of CVE-2024-37085 (CVSS score: 6.8), an Active Directory integration authentication bypass that allows an attacker to obtain administrative access to the host.
“A malicious actor with sufficient Active Directory (AD) permissions can gain full access to an ESXi host that was previously configured to use AD for user management by re-creating the configured AD group (‘ESXi Admins’ by default) after it was deleted from AD,” Broadcom-owned VMware noted in an advisory released in late June 2024.
In other words, escalating privileges on ESXi to the administrator was as simple as creating a new AD group named “ESX Admins” and adding any user to it, or renaming any group in the domain to “ESX Admins” and adding a user to the group or using an existing group member.
Microsoft, in a new analysis published on July 29, said it observed ransomware operators like Storm-0506, Storm-1175, Octo Tempest, and Manatee Tempest leveraging the post-compromise technique to deploy Akira and Black Basta.
“VMware ESXi hypervisors joined to an Active Directory domain consider any member of a domain group named ‘ESX Admins’ to have full administrative access by default,” researchers Danielle Kuznets Nohi, Edan Zwick, Meitar Pinto, Charles-Edouard Bettan, and Vaibhav Deshmukh said.
“This group is not a built-in group in Active Directory and does not exist by default. ESXi hypervisors do not validate that such a group exists when the server is joined to a domain and still treats any members of a group with this name with full administrative access, even if the group did not originally exist.”
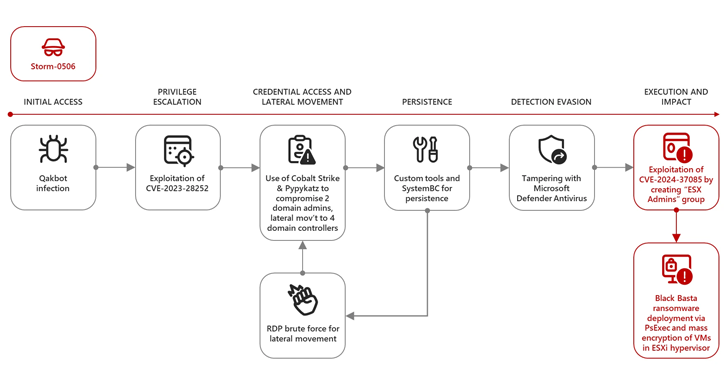
In one attack staged by Storm-0506 against an unnamed engineering firm in North America, the threat actor weaponized the vulnerability to gain elevated permissions to the ESXi hypervisors after having obtained an initial foothold using a QakBot infection and exploiting another flaw in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) Driver (CVE-2023-28252, CVSS score: 7.8) for privilege escalation.
Subsequently, phases entailed the deployment of Cobalt Strike and Pypykatz, a Python version of Mimikatz, to steal domain administrator credentials and move laterally across the network, followed by dropping the SystemBC implant for persistence and abusing the ESXi admin access to deploy Black Basta.
“The actor was also observed attempting to brute force Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connections to multiple devices as another method for lateral movement, and then again installing Cobalt Strike and SystemBC,” the researchers said. “The threat actor then tried to tamper with Microsoft Defender Antivirus using various tools to avoid detection.”

The development comes as Google-owned Mandiant revealed that a financially motivated threat cluster called UNC4393 is using initial access obtained via a C/C++ backdoor codenamed ZLoader (aka DELoader, Terdot, or Silent Night) to deliver Black Basta, moving away from QakBot and DarkGate.
“UNC4393 has demonstrated a willingness to cooperate with multiple distribution clusters to complete its actions on objectives,” the threat intelligence firm said. “This most recent surge of Silent Night activity, beginning earlier this year, has been primarily delivered via malvertising. This marked a notable shift away from phishing as UNC4393’s only known means of initial access.”
The attack sequence involves making use of the initial access to drop Cobalt Strike Beacon and a combination of custom and readily-available tools to conduct reconnaissance, not to mention relying on RDP and Server Message Block (SMB) for lateral movement. Persistence is achieved by means of SystemBC.
ZLoader, which resurfaced after a long gap late last year, has been under active development, with new variants of the malware being propagated via a PowerShell backdoor referred to as PowerDash, per recent findings from Walmart’s cyber intelligence team.
Over the past few years, ransomware actors have demonstrated an appetite for latching onto novel techniques to maximize impact and evade detection, increasingly targeting ESXi hypervisors and taking advantage of newly disclosed security flaws in internet-facing servers to breach targets of interest.
Qilin (aka Agenda), for instance, was originally developed in the Go programming language, but has since been redeveloped using Rust, indicating a shift towards constructing malware using memory-safe languages. Recent attacks involving ransomware have been found to leverage known weaknesses in Fortinet and Veeam Backup & Replication software for initial access.
“The Qilin ransomware is capable of self-propagation across a local network,” Group-IB said in a recent analysis, adding it’s also equipped to “carry out self-distribution using VMware vCenter.”
Another notable malware employed in Qilin ransomware attacks is a tool dubbed Killer Ultra that’s designed to disable popular endpoint detection and response (EDR) software running on the infected host as well as clear all Windows event logs to remove all indicators of compromise.
Organizations are recommended to install the latest software updates, practice credential hygiene, enforce two-factor authentication, and take steps to safeguard critical assets using appropriate monitoring procedures and backup and recovery plans.