Cybersecurity researchers are sounding the alarm over an ongoing campaign that’s leveraging internet-exposed Selenium Grid services for illicit cryptocurrency mining.
Cloud security firm Wiz is tracking the activity under the name SeleniumGreed. The campaign, which is targeting older versions of Selenium (3.141.59 and prior), is believed to be underway since at least April 2023.
“Unbeknownst to most users, Selenium WebDriver API enables full interaction with the machine itself, including reading and downloading files, and running remote commands,” Wiz researchers Avigayil Mechtinger, Gili Tikochinski, and Dor Laska said.
“By default, authentication is not enabled for this service. This means that many publicly accessible instances are misconfigured and can be accessed by anyone and abused for malicious purposes.”
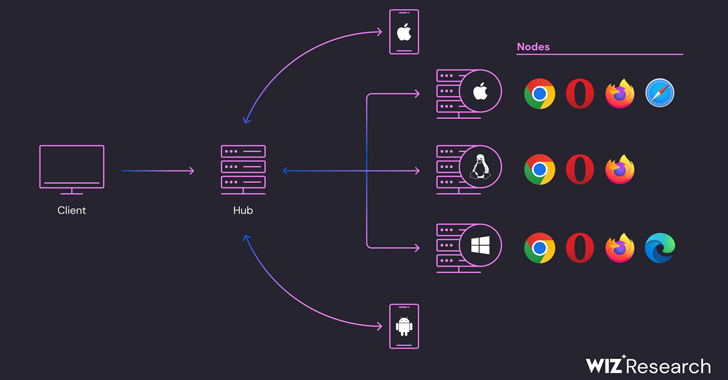
Selenium Grid, part of the Selenium automated testing framework, enables parallel execution of tests across multiple workloads, different browsers, and various browser versions.

“Selenium Grid must be protected from external access using appropriate firewall permissions,” the project maintainers warn in a support documentation, stating that failing to do so could allow third-parties to run arbitrary binaries and access internal web applications and files.
Exactly who is behind the attack campaign is currently not known. However, it involves the threat actor targeting publicly exposed instances of Selenium Grid and making use of the WebDriver API to run Python code responsible for downloading and running an XMRig miner.
It starts with the adversary sending a request to the vulnerable Selenium Grid hub with an aim to execute a Python program containing a Base64-encoded payload that spawns a reverse shell to an attacker-controlled server (“164.90.149[.]104”) in order to fetch the final payload, a modified version of the open-source XMRig miner.
“Instead of hardcoding the pool IP in the miner configuration, they dynamically generate it at runtime,” the researchers explained. “They also set XMRig’s TLS-fingerprint feature within the added code (and within the configuration), ensuring the miner will only communicate with servers controlled by the threat actor.”
The IP address in question is said to belong to a legitimate service that has been compromised by the threat actor, as it has also been found to host a publicly exposed Selenium Grid instance.
Wiz said it’s possible to execute remote commands on newer versions of Selenium and that it identified more than 30,000 instances exposed to remote command execution, making it imperative that users take steps to close the misconfiguration.
“Selenium Grid is not designed to be exposed to the internet and its default configuration has no authentication enabled, so any user that has network access to the hub can interact with the nodes via API,” the researchers said.
“This poses a significant security risk if the service is deployed on a machine with a public IP that has inadequate firewall policy.”
Update #
Selenium, in an advisory released on July 31, 2024, urged users to upgrade their instances to the latest version to mitigate against the threat.
“Selenium Grid by default doesn’t have any authentication as the assumption has always been that we want you to put this behind a secure network to prevent people from abusing your resources,” it said. “Another way to combat this is to use a cloud provider to run your Selenium Grid.”