Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a privilege escalation vulnerability impacting Google Cloud Platform’s Cloud Functions service that an attacker could exploit to access other services and sensitive data in an unauthorized manner.
Tenable has given the vulnerability the name ConfusedFunction.
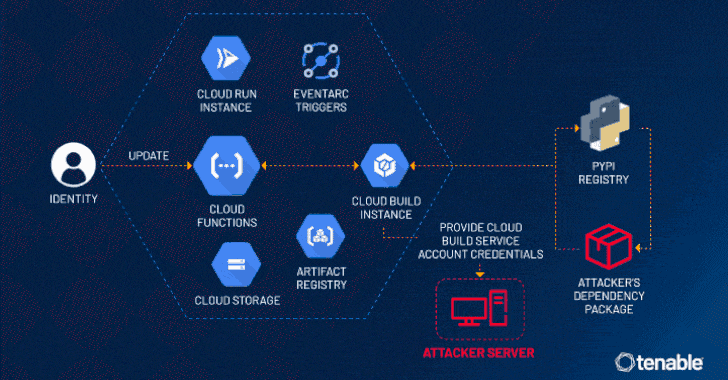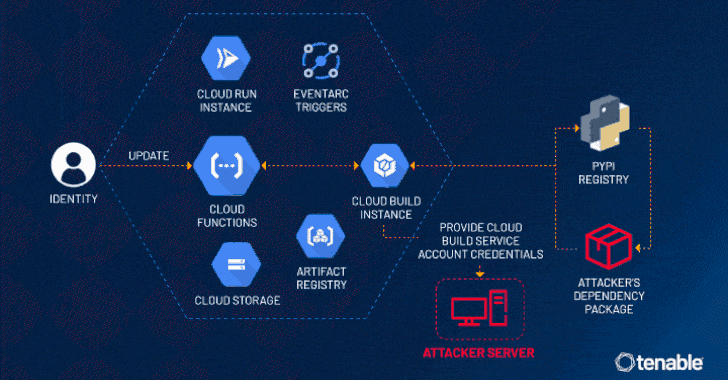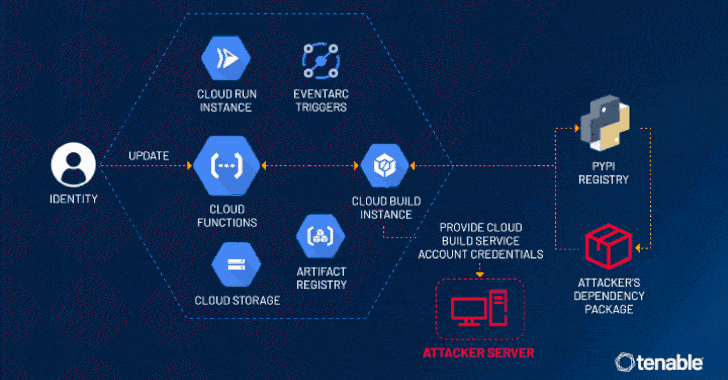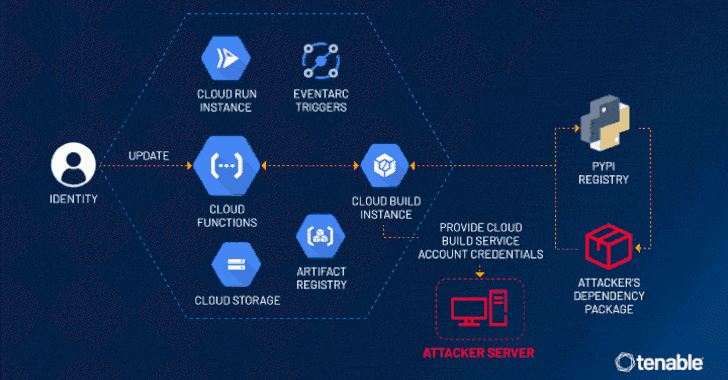
“An attacker could escalate their privileges to the Default Cloud Build Service Account and access numerous services such as Cloud Build, storage (including the source code of other functions), artifact registry and container registry,” the exposure management company said in a statement.
“This access allows for lateral movement and privilege escalation in a victim’s project, to access unauthorized data and even update or delete it.”
Cloud Functions refers to a serverless execution environment that allows developers to create single-purpose functions that are triggered in response to specific Cloud events without the need to manage a server or update frameworks.
The problem discovered by Tenable has to do with the fact that a Cloud Build service account is created in the background and linked to a Cloud Build instance by default when a Cloud Function is created or updated.
This service account opens the door for potential malicious activity owing to its excessive permissions, thereby permitting an attacker with access to create or update a Cloud Function to leverage this loophole and escalate their privileges to the service account.
This permission could then be abused to access other Google Cloud services that are also created in tandem with the Cloud Function, including Cloud Storage, Artifact Registry, and Container Registry. In a hypothetical attack scenario, ConfusedFunction could be exploited to leak the Cloud Build service account token via a webhook.

Following responsible disclosure, Google has updated the default behavior such that Cloud Build uses the Compute Engine default service account to prevent misuse. However, it’s worth noting that these changes do not apply to existing instances.
“The ConfusedFunction vulnerability highlights the problematic scenarios that may arise due to software complexity and inter-service communication in a cloud provider’s services,” Tenable researcher Liv Matan said.
“While the GCP fix has reduced the severity of the problem for future deployments, it didn’t completely eliminate it. That’s because the deployment of a Cloud Function still triggers the creation of the aforementioned GCP services. As a result, users must still assign minimum but still relatively broad permissions to the Cloud Build service account as part of a function’s deployment.”
The development comes as Outpost24 detailed a medium-severity cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw in the Oracle Integration Cloud Platform that could be weaponized to inject malicious code into the application.
The flaw, which is rooted in the handling of the “consumer_url” parameter, was resolved by Oracle in its Critical Patch Update (CPU) released earlier this month.
“The page for creating a new integration, found at https://<instanceid>.integration.ocp.oraclecloud.com/ic/integration/home/faces/link?page=integration&consumer_url=<payload>, did not require any other parameters,” security researcher Filip Nyquist said.

“This meant that an attacker would only need to identify the instance-id of the specific integration platform to send a functional payload to any user of the platform. Consequently, the attacker could bypass the requirement of knowing a specific integration ID, which is typically accessible only to logged-in users.”
It also follows Assetnote’s discovery of three security vulnerabilities in the ServiceNow cloud computing platform (CVE-2024-4879, CVE-2024-5178, and CVE-2024-5217) that could be fashioned into an exploit chain in order to gain full database access and execute arbitrary code on the within the context of the Now Platform.
The ServiceNow shortcomings have since come under active exploitation by unknown threat actors as part of a “global reconnaissance campaign” designed to gather database details, such as user lists and account credentials, from susceptible instances.
The activity, targeting companies in various industry verticals such as energy, data centers, software development, and government entities in the Middle East, could be leveraged for “cyber espionage and further targeting,” Resecurity said.
ServiceNow, in a statement shared with The Hacker News said it has “not observed evidence that the activity […] is related to instances that ServiceNow hosts.
“We have encouraged our self-hosted and ServiceNow-hosted customers to apply relevant patches if they have not already done so. We will also continue to work directly with customers who need assistance in applying those patches. It is important to note that these are not new vulnerabilities, but rather were previously addressed and disclosed in CVE-2024-4879, CVE-2024-5217, and CVE-2024-5178.”
(The story was updated after publication to include details about active exploitation of ServiceNow flaws.)