South Korea’s National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) reported that North Korea-linked hackers hijacked VPN software updates to deploy malware.
South Korea’s national security and intelligence agencies, including the National Intelligence Service, the Prosecutor’s Office, the Police Agency, the Military Intelligence Command, and the Cyber Operations Command, have issued a joint cybersecurity advisory to warn that North Korea-linked hackers exploited VPN software update to install malware on target networks.
According to the South Korean authorities, the government of Pyongyang’s goal is to steal intellectual property and trade secrets from the South.
North Korea-linked actors hacking groups are targeting South Korea’s construction and machinery industries. The advisory provides details on the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by the attackers, as well as indicators of compromise (IoCs) for these attacks.
“Following the official announcement of the “Local Development 20×10 Policy” by Kim Jong-un at the 14th Supreme People’s Assembly on January 15 this year, North Korea has been pushing for the construction of modern industrial plants in 20 cities and counties annually. North Korean hacking organizations are also intensifying their efforts to support this policy.” reads the advisory. “It is suspected that North Korean hackers are stealing data from South Korea’s construction, machinery, and urban development sectors to support their industrial plant construction and local development plans.”
The North Korean APT groups Kimsuky and Andariel, both linked to the Reconnaissance General Bureau, are the main hacking groups involved. Their simultaneous and targeted attacks on specific sectors are considered unusual and experts highlighted that they necessitate careful preparation.
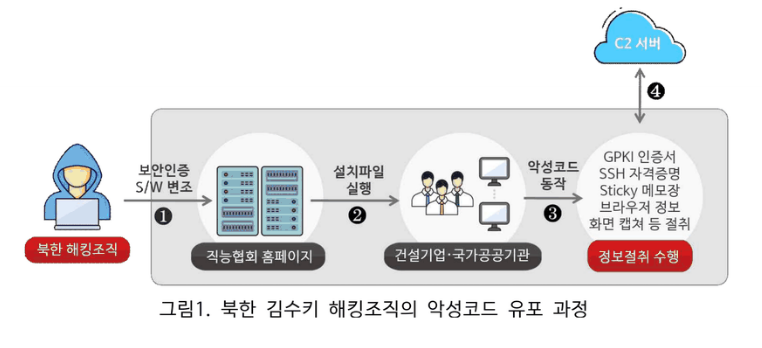
In January 2024, the Kimsuky APT group was spotted distributing malware through the website of a construction industry association in South Korea. The malware was concealed within security authentication software used during website login. The attack aimed at infecting PCs belonging to personnel from local governments, public institutions, and construction companies who accessed the site. This attack combined a “supply chain attack,” which involved tampering with legitimate distribution channels, with a “watering hole attack,” targeting websites frequently visited by construction and design professionals.
“When the tampered security authentication software installation file is executed, malware in the form of a DLL is run in the %APPDATA% directory, along with legitimate programs. This malware operates in the background to steal information, making it difficult for users to notice malicious activities. The malware, written in Go, is identified by some security firms as ‘TrollAgent’.” reads the advisory. “The malware has functionalities to collect system information, capture user screens, and gather information stored in browsers (credentials, cookies, bookmarks, history). It can also steal GPKI certificates, SSH keys, Sticky Notes, and FileZilla information from the infected PC.”

Another case detailed by the researchers took place in April 2024, when the Andariel hacking group exploited vulnerabilities in domestic VPN and server security software to distribute remote control malware, DoraRAT, to construction and machinery companies. The attackers manipulated the VPN client-server communication protocol to disguise malicious update files as legitimate ones. The compromised VPN client mistakenly accepted these files, leading to the execution of DoraRAT.
“The remote control malware (DoraRAT) used in the attack was simple and lightweight, focusing on basic functions like file upload/download and command execution. It was distributed using a watering hole technique, which increased its exposure. Unlike more sophisticated APT malware, DoraRAT had minimal functionality. Additionally, a file-stealing variant was identified, capable of exfiltrating large files related to machinery and equipment design.” continues the joint advisory. “Andariel also exploited vulnerabilities in server security products, demonstrating a trend of targeting IT management software for mass infections due to their high-level access and control.”
Below are the mitigations provided by North Korean authorities:
- Organizations managing websites in sectors like construction and machinery should seek security assessments from relevant institutions if needed.
- Ongoing security training for all organizational members, including IT and security staff, is crucial.
- Keep operating systems and applications up-to-date, and use updated antivirus software with real-time detection.
- Implement strict approval policies for software distribution to prevent vulnerabilities in automated deployment.
- Stay informed about government cybersecurity advisories and act promptly on manufacturer recommendations.
- Refer to guidelines for software supply chain security and software development security provided by national authorities.