
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up and Using the Custom Search API in Google Colab
Introduction:
Have you ever wished for a more personalized search engine that caters exclusively to your preferences and trusted sources? In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to create your own custom search engine using Google’s Programmable Search Engine and call the Custom Search API in Google Colab using Python. Say hello to your very own, tailored Google!
Step 1: Set Up the Custom Search API
- Visit the Google Developers Console: https://console.developers.google.com/
2. Create a new project by clicking on the “Select a project” dropdown menu at the top right corner of the page, then click on “New Project.”

3. Enter your project name, then click “Create.”

4. Navigate to the “Dashboard” tab on the left panel, click “Enable APIs and Services,” and search for “Custom Search API.”
5. Enable the Custom Search API and create credentials (API key) by clicking on “Create Credentials.”

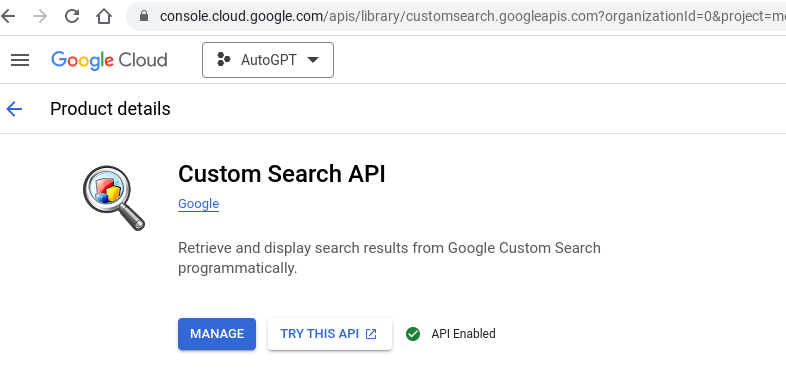

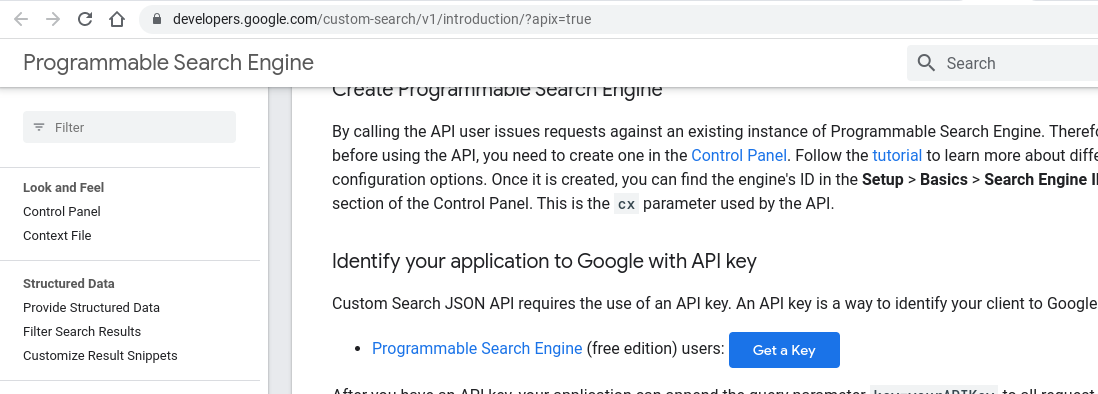
You would think that creating your API would be enough but it is not. After you select MANAGE and you enable your key, you must select TRY IN API EXPLORER and in that page you have to select “Get a Key” and only then will you have the key that you need.

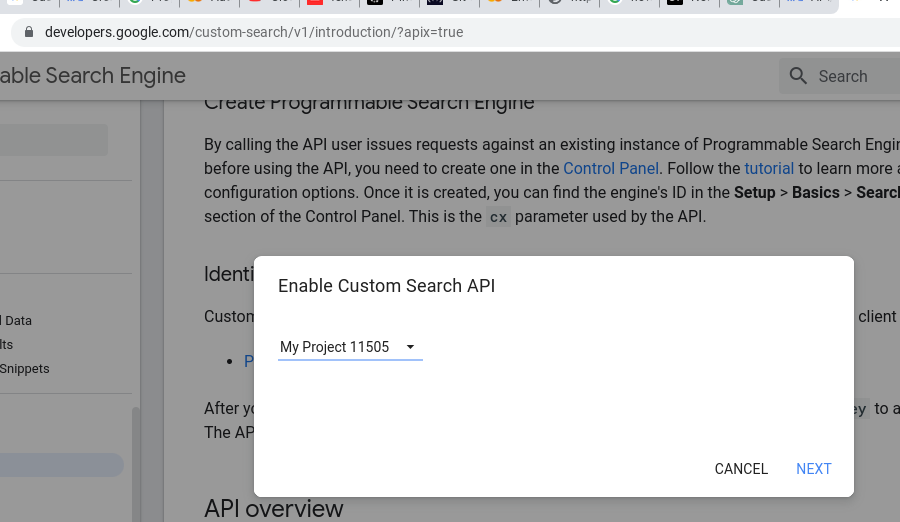
6. Keep your API key handy, as we will use it to make API calls.
Step 2: Create Your Custom Search Engine
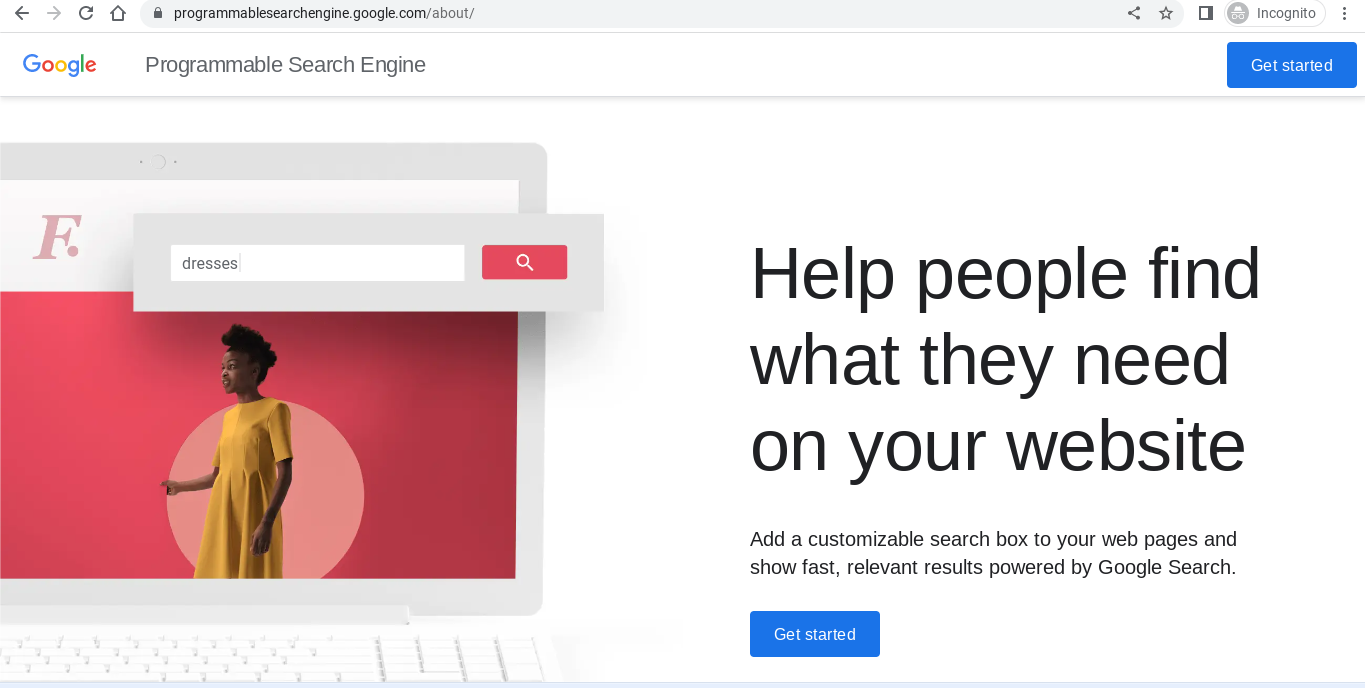
2. Click “Get Started” and sign in with your Google account.
3. Click “New search engine” and follow the steps to set up your custom search engine.
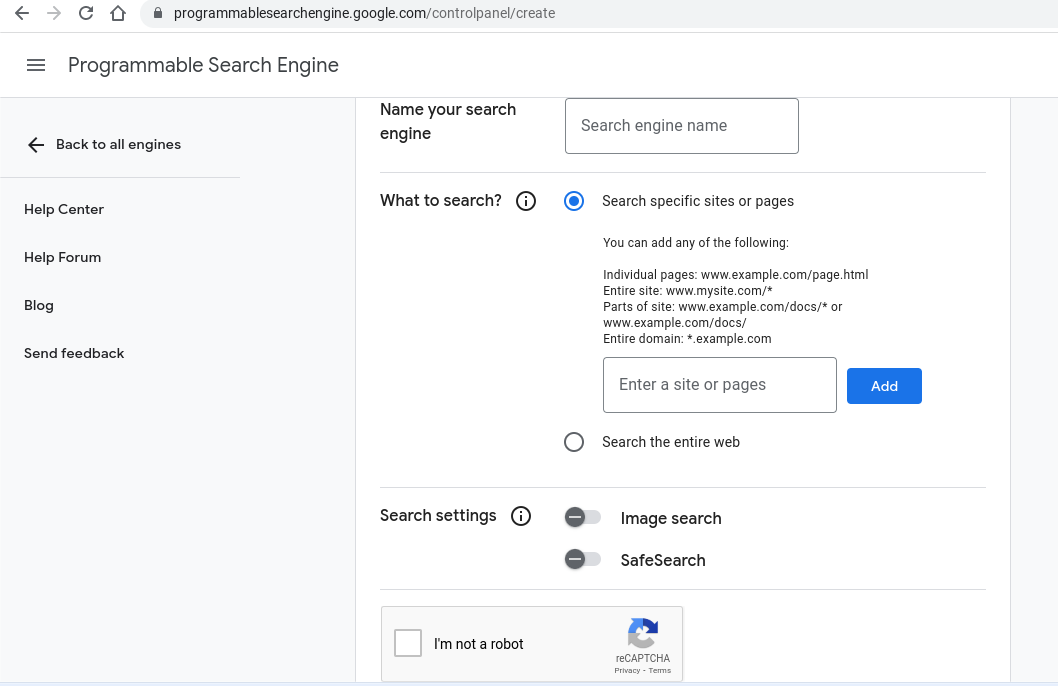
- Enter sites to search (e.g., “https://www.nytimes.com/” or “https://www.bbc.com/“).
- Name your search engine.
- Click “Create.”
4. Customize your search engine by configuring settings under the “Basics” and “Sites to search” tabs.
5. Navigate to the “Setup” tab to retrieve your “cx” parameter, which is the search engine ID.
Step 3: Use Google Colab to Call the Custom Search API
- Visit https://colab.research.google.com/ and sign in with your Google account.
- Click “File” > “New notebook” to create a new Python notebook.
Step 4: Install Required Libraries and Set Up API Calls
import requests
import json
import pandas as pd
api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY"
cx = "YOUR_CX"
query = "Your Search Query Here"
url = f"https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1?key={api_key}&cx={cx}&q={query}"
response = requests.get(url)
data = json.loads(response.text)
# Check for errors or empty search results
if 'error' in data:
print("Error:", data['error']['message'])
elif 'items' not in data:
print("No search results found.")
else:
# Extract search results
search_results = data['items']
# Create a pandas DataFrame
columns = ['Title', 'Link', 'Snippet']
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=columns)
for result in search_results:
title = result['title']
link = result['link']
snippet = result['snippet']
df = df.append({'Title': title, 'Link': link, 'Snippet': snippet}, ignore_index=True)
# Display the DataFrame
print(df)
Step 5: Execute Your Custom Search
- Replace “Your Search Query Here” with a query of your choice.
- Run the code to see the search results in a pandas DataFrame.

Conclusion:
You’ve now built your very own custom search engine using Google’s Programmable Search Engine and learned how to call the Custom Search API in Google Colab using Python. With this powerful tool, you can tailor search results to your preferences and trusted sources. It’s time to enjoy the power of personalized search and unlock the full potential of Google search for your needs!