In a revealing new study, cybersecurity researchers from Germany have highlighted significant vulnerabilities and operational challenges within the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) protocol, raising serious concerns about its current stability and security. While the protocol was designed to bolster the safety of internet traffic routing, researchers suggest it may fall short of its promises.
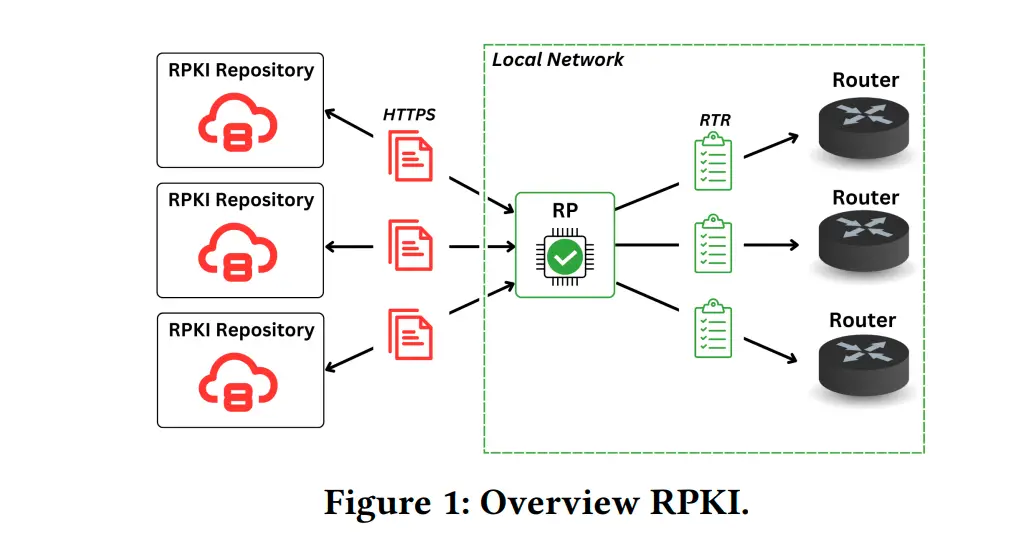
RPKI was introduced as a remedy for the inherent flaws in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), the backbone of internet traffic routing, which lacked essential security measures. RPKI enhances security by enabling network operators to verify the authenticity of BGP route origins through Route Origin Validation (ROV) and Route Origin Authorizations (ROA). In theory, this system should prevent the announcement of fraudulent or malicious routes. However, the study from Germany reveals that RPKI is far from infallible, with numerous vulnerabilities that could undermine its core purpose.
In early September, the White House integrated RPKI into its network infrastructure as part of a broader initiative to improve the security of the Internet, specifically targeting national security and economic vulnerabilities in the U.S. The decision was lauded as a forward-thinking move to address critical internet security gaps. Yet, just weeks later, this German report casts a shadow of doubt over the efficacy of RPKI.
The research outlines 53 vulnerabilities within RPKI’s software components, including critical issues such as Denial of Service (DoS), authentication bypass, cache poisoning, and even remote code execution. While many of these vulnerabilities were quickly patched, the rapid discovery of so many flaws raises alarm bells about the overall robustness of the protocol.
The study warns that RPKI, in its current iteration, is an attractive target for cybercriminals. The myriad vulnerabilities identified could lead to failures in the validation process, opening doors to significant attacks on the internet’s routing infrastructure. Worse yet, these flaws may even provide access to local networks where vulnerable RPKI software is in use.
One of the researchers’ gravest concerns is the potential for supply chain attacks, where cybercriminals could implant backdoors in the open-source components of RPKI. This could lead to a widespread compromise of the very systems meant to secure internet traffic routing.
Moreover, many operators have encountered difficulties in updating the RPKI code due to the lack of automation in the process. This bottleneck could delay crucial security patches, leaving around 41.2% of RPKI users exposed to at least one known attack.
Experts also raise questions about the U.S. government’s timing in adopting a protocol that may not yet be fully mature. While the White House’s efforts to bolster cybersecurity are commendable, the rapid deployment of RPKI before it reaches its full potential could have unintended consequences. The lack of automation and scalability tools further exacerbates the problem, as incorrect configurations or delayed updates could severely impair the protocol’s effectiveness.
Nonetheless, the researchers recognize that most internet technologies were introduced with imperfections and have evolved over time through practical use. They suggest that while Resource Public Key Infrastructure is not flawless, its adoption can still be a crucial step in strengthening internet security, provided it is continuously improved upon.