Kaspersky Labs has recently revealed a major cyber-espionage campaign conducted by the Lazarus group, dubbed “Operation SyncHole.” Targeting critical industries in South Korea, including software, IT, financial, semiconductor manufacturing, and telecommunications sectors, this operation exemplifies the group’s sophisticated and evolving tactics.
“We have been tracking the latest attack campaign by the Lazarus group since last November,” Kaspersky reported, emphasizing that the attackers used a combination of watering hole strategies and the exploitation of vulnerabilities within South Korean software to penetrate defenses.
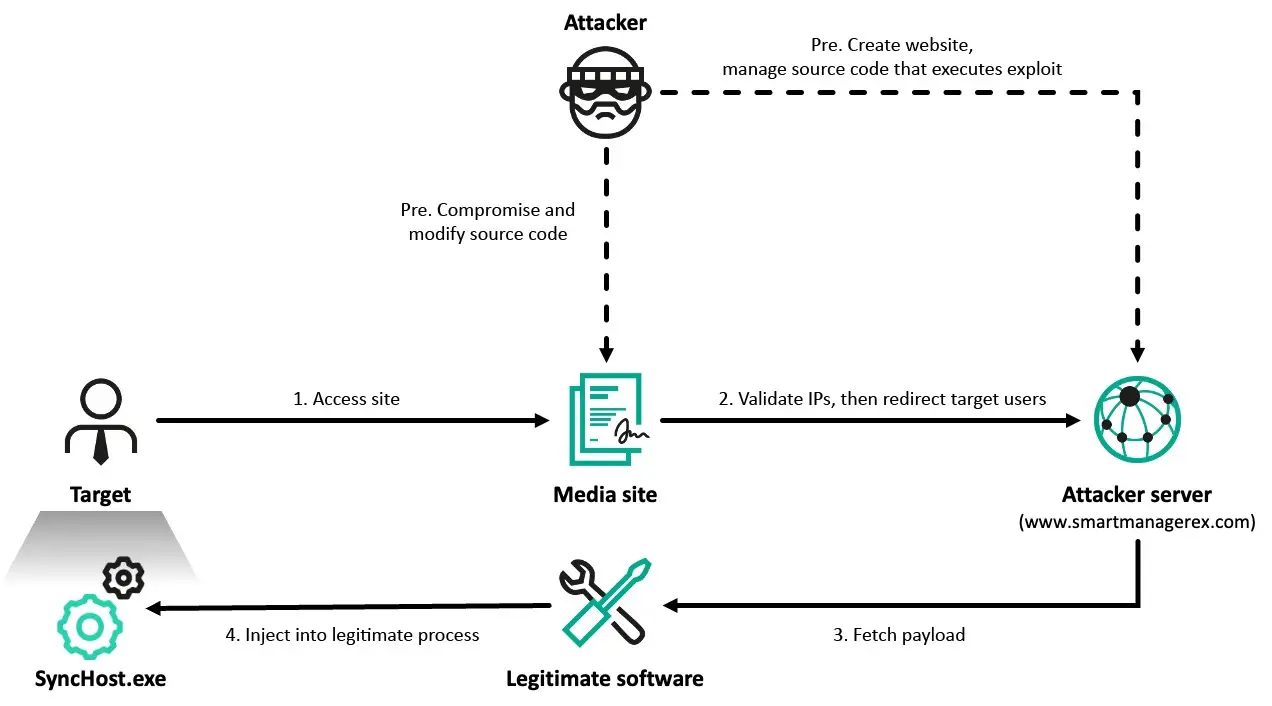
The operation began with a watering hole attack, where visitors to compromised South Korean online media sites were selectively redirected to attacker-controlled pages. “Shortly after visiting one particular site, the machine was compromised by the ThreatNeedle malware,” Kaspersky noted. The attackers exploited a potential flaw in Cross EX software, allowing them to inject malware into legitimate processes like SyncHost.exe.

Further investigation uncovered that Lazarus also leveraged a one-day vulnerability in Innorix Agent to facilitate lateral movement within networks. This vulnerability allowed attackers to deliver additional malware on a targeted host of their choice, exploiting traffic validation weaknesses.
Kaspersky identified multiple Lazarus malware strains with new capabilities, including:
- ThreatNeedle (updated variant): Divided into Loader and Core components, utilizing the Curve25519 algorithm and ChaCha20 encryption.
- wAgent (variant): An upgraded downloader capable of in-memory payload execution and complex plugin management.
- Agamemnon Downloader: Implementing advanced reflective loading techniques to bypass EDRs.
- SIGNBT (versions 0.0.1 and 1.2): Shifted towards minimized remote control and scheduled execution.
- COPPERHEDGE: Used primarily for internal reconnaissance, exploiting ADS for stealthy communication with C2 servers.
“The malware used by the Lazarus group has been rapidly evolving to include lightweighting and modularization,” Kaspersky remarked, indicating a broader strategic shift towards stealthier and more flexible operations.
The attackers cleverly used compromised legitimate South Korean websites as C2 servers, blending malicious activities with normal traffic. Kaspersky also noted that domains like smartmanagerex[.]com and re-registered domains such as thek-portal[.]com were utilized in the campaign.
Attribution to Lazarus was supported by toolset signatures, TTP analysis, and operational timings: “The timeframes were mostly concentrated between GMT 00:00 and 09:00,” aligning with GMT+09, South Korea’s and North Korea’s time zones.
Upon discovery, Kaspersky promptly communicated the findings to the Korea Internet & Security Agency (KrCERT/CC), ensuring swift remediation. Vulnerabilities in Cross EX and Innorix Agent have since been patched, mitigating the immediate threats.