
In January 2025, Ivanti published an advisory[1] regarding the vulnerability CVE-2025-0282 in Ivanti Connect Secure. JPCERT/CC has confirmed multiple cases of this vulnerability being exploited in Japan since late December 2024, prior to the disclosure of the vulnerability, and published a security alert[2]. This vulnerability has already been used by multiple attack groups.
Among these cases, JPCERT/CC has confirmed that SPAWN malware family[3][4], which infects after exploiting the vulnerability, according to a report by Google, had been updated. This article explains the updated malware family (hereafter referred to as “SPAWNCHIMERA”).
Overview of SPAWNCHIMERA’s behavior
Figure 1 shows an overview of SPAWNCHIMERA’s behavior. It is malware with the functions of SPAWNANT, SPAWNMOLE, and SPAWNSNAIL all updated and integrated. Therefore, there is no significant difference in the way malware is installed or injected into other processes compared to SPAWN family reported by Google[4]. On the other hand, as shown in Figure 1, SPAWNCHIMERA can be injected into various processes and run in each of them. The major changes are as follows.
- Change in inter-process communication
- Function to fix vulnerability CVE-2025-0282
- New decode functions added
- Deleted debug message
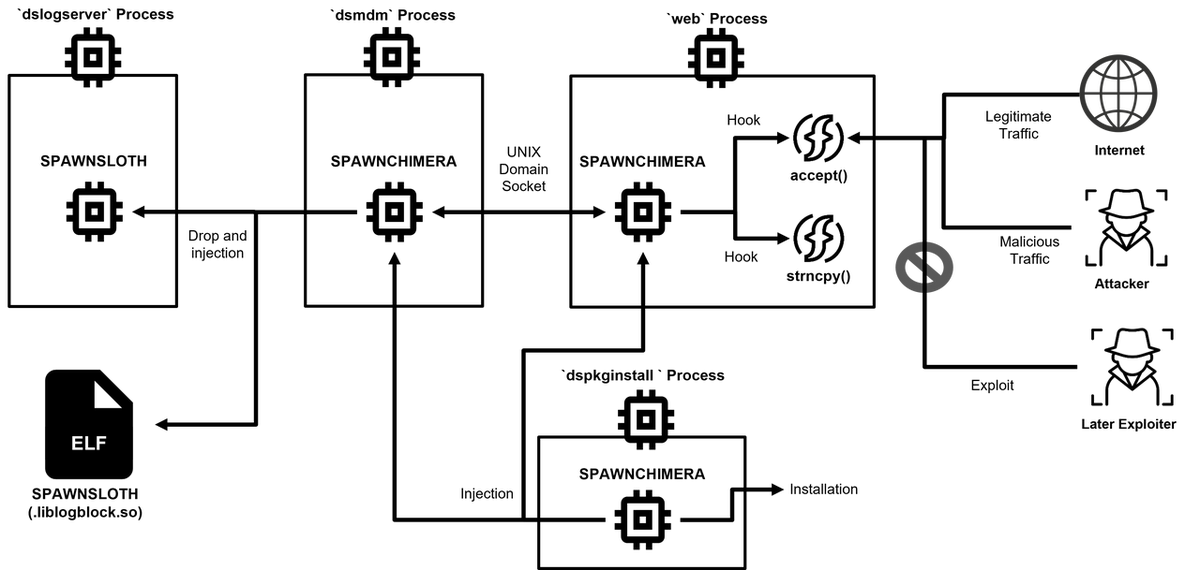
Figure 1: Flow of SPAWNCHIMERA’s behavior.
Inter-process communication through UNIX domain sockets
In the previous SPAWN family, the malicious traffic received by SPAWNMOLE was sent to port 8300 on 127.0.0.1, and SPAWNSNAIL processed it. With the abovementioned update, this inter-process communication method was altered to use UNIX domain socket. It is created in the below path, and malicious traffic is sent and received between SPAWNCHIMERA injected into the web process and that injected into the dsmdm process. This change made it more difficult to detect the malware, as netstat command results from the Integrity Checker Tool (ICT) may not be displayed.
/home/runtime/tmp/.logsrv
Function to fix the vulnerability CVE-2025-0282
SPAWNCHIMERA has a new function to fix the CVE-2025-0282 vulnerability. CVE-2025-0282 is a buffer overflow vulnerability[5] caused by the strncpy function, and the malware dynamically fixes it by hooking the strncpy function and limiting the copy size to 256. Figure 2 shows the replaced strncpy function. SPAWNCHIMERA converts its process name to hexadecimal and verifies the added value. The fix is triggered when the process name is “web” The fix is programmed to be disabled when the first byte of the source copied to the strncpy function matches 0x04050203. Due to this function, if another attacker uses this vulnerability to attempt penetration or executes a PoC[6] for scanning purposes, the attack may not succeed.
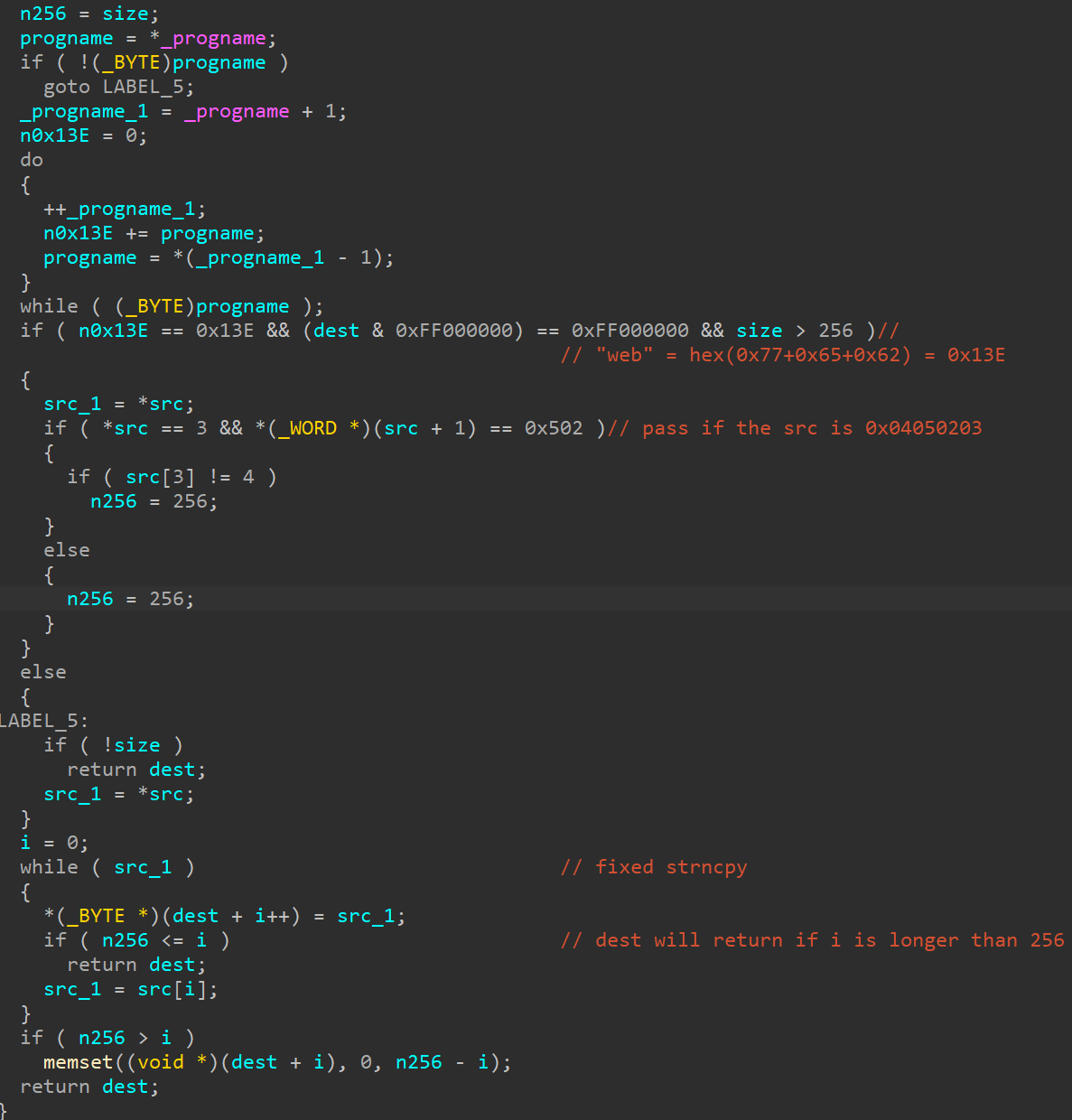
Figure 2: The strncpy function replaced through hook
New decode functions added
In the previous samples, the private key for SSH server functionality was hardcoded in plaintext within the samples and exported to /tmp/.dskey. On the other hand, in SPAWNCHIMERA, it is now encoded and hardcoded within the sample. The key is used after being decoded with an XOR-based decode function. Since it is not exported as a file, traces are less likely to be left. The decoded private key is shown below.
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY----- b3BlbnNzaC1rZXktdjEAAAAABG5vbmUAAAAEbm9uZQAAAAAAAAABAAAAMwAAAAtzc2gtZW QyNTUxOQAAACB5yHbNy5qrd638t2dCLQ08TJb3D8m0+vifkGmBRho6+QAAAJB08wxcdPMM XAAAAAtzc2gtZWQyNTUxOQAAACB5yHbNy5qrd638t2dCLQ08TJb3D8m0+vifkGmBRho6+Q AAAEBqjrwB7thqk5LnigfsE8EqlKrmWNhy82k5GTV8BBVlDXnIds3Lmqt3rfy3Z0ItDTxM lvcPybT6+J+QaYFGGjr5AAAACWthbGlAa2FsaQECAwQ= -----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
Additionally, while the previous sample identified malicious traffic in replaced accept function, by matching a part of the received buffer with a hard-coded value, SPAWNCHIMERA has a new decode function and determines whether the traffic is malicious based on its calculation result. The decode function is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3: Decode function used to identify malicious traffic
Deleted debug message
While there are only minor differences in functionality between the previous SPAWNSLOTH and that dropped by SPAWNCHIMERA, some functions related to debug messages were deleted from the entire sample, possibly with the aim of complicating analysis and preventing hunting. This modification is also seen in the main sample of SPAWNCHIMERA. Figure 4 shows an example of the deleted functions.
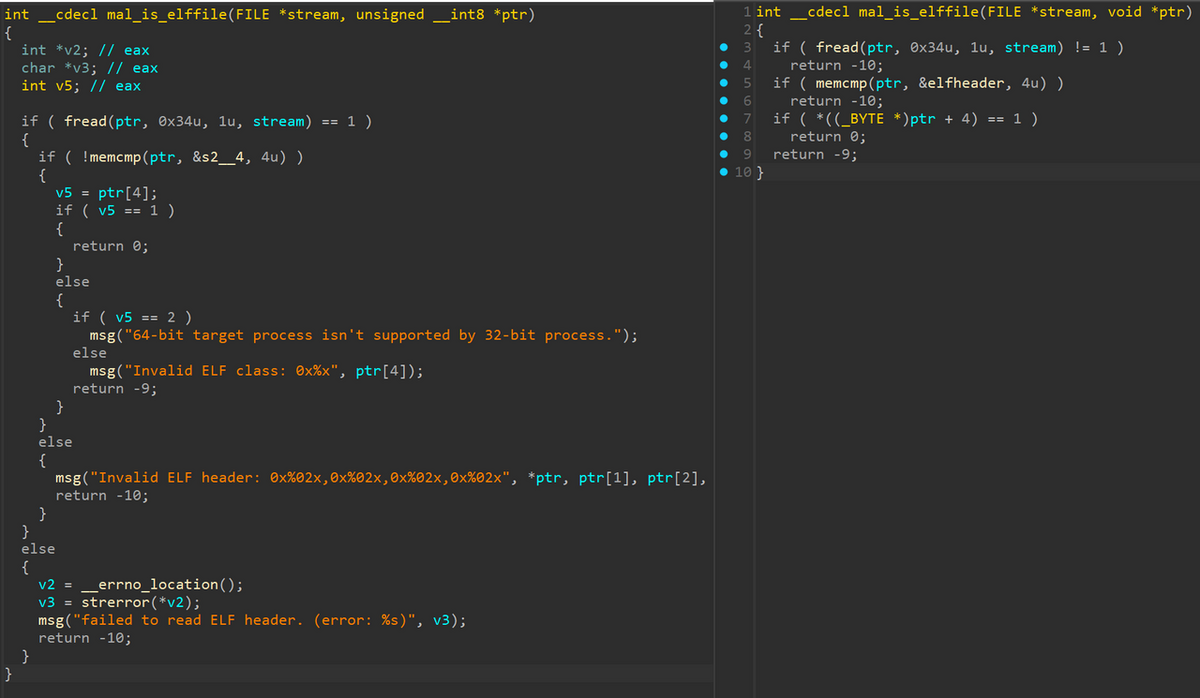
Figure 4: Deleted debug message (left: previous version, right: current version)
In closing
SPAWNCHIMERA has evolved into more sophisticated malware by changing various functions of SPAWN family in a way that leaves less traces, and SPAWN family is expected to remain in use. We hope that the information in this article will help your malware analysis. The hash values and file paths of the confirmed malware are listed in the Appendix.
Yuma Masubuchi
(Translated by Takumi Nakano)
References
[1] Ivanti
Security Advisory Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure & ZTA Gateways (CVE-2025-0282, CVE-2025-0283)
https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/Security-Advisory-Ivanti-Connect-Secure-Policy-Secure-ZTA-Gateways-CVE-2025-0282-CVE-2025-0283?language=en_US
[2] JPCERT/CC
Ivanti Connect Secureなどにおける脆弱性(CVE-2025-0282)に関する注意喚起
https://www.jpcert.or.jp/at/2025/at250001.html
[3] Google
Ivanti Connect Secure VPN Targeted in New Zero-Day Exploitation
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/ivanti-connect-secure-vpn-zero-day/?hl=en
[4] Google
Cutting Edge, Part 4: Ivanti Connect Secure VPN Post-Exploitation Lateral Movement Case Studies
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/ivanti-post-exploitation-lateral-movement?hl=en
[5] watchTowr Labs
Do Secure-By-Design Pledges Come With Stickers? – Ivanti Connect Secure RCE (CVE-2025-0282)
https://labs.watchtowr.com/do-secure-by-design-pledges-come-with-stickers-ivanti-connect-secure-rce-cve-2025-0282/
[6] Stephen Fewer
CVE-2025-0282.rb
https://github.com/sfewer-r7/CVE-2025-0282/blob/main/CVE-2025-0282.rb
Appendix A: Hash values of the malware
- SPAWNCHIMERA 94b1087af3120ae22cea734d9eea88ede4ad5abe4bdeab2cc890e893c09be955
- SPAWNSLOTH 9bdf41a178e09f65bf1981c86324cd40cb27054bf34228efdcfee880f8014baf
Appendix B: File paths of the malware confirmed
- SPAWNCHIMERA /lib/libdsupgrade.so
- SPAWNSLOTH /tmp/.liblogblock.so