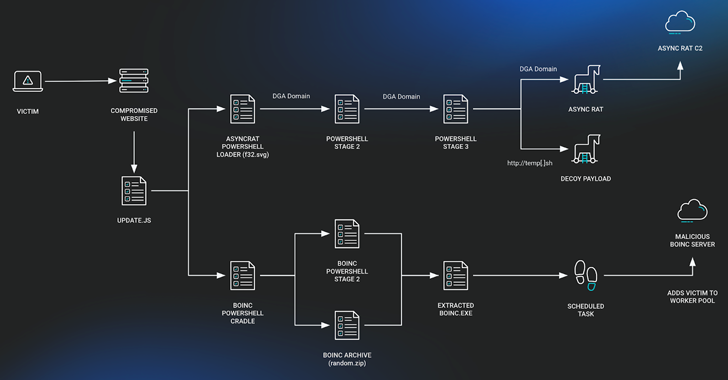
The JavaScript downloader malware known as SocGholish (aka FakeUpdates) is being used to deliver a remote access trojan called AsyncRAT as well as a legitimate open-source project called BOINC.
BOINC, short for Berkeley Open Infrastructure Network Computing Client, is an open-source “volunteer computing” platform maintained by the University of California with an aim to carry out “large-scale distributed high-throughput computing” using participating home computers on which the app is installed.
“It’s similar to a cryptocurrency miner in that way (using computer resources to do work), and it’s actually designed to reward users with a specific type of cryptocurrency called Gridcoin, designed for this purpose,” Huntress researchers Matt Anderson, Alden Schmidt, and Greg Linares said in a report published last week.
These malicious installations are designed to connect to an actor-controlled domain (“rosettahome[.]cn” or “rosettahome[.]top”), essentially acting as a command-and-control (C2) server to collect host data, transmit payloads, and push further commands. As of July 15, 10,032 clients are connected to the two domains.
The cybersecurity firm said while it hasn’t observed any follow-on activity or tasks being executed by the infected hosts, it hypothesized that the “host connections could be sold off as initial access vectors to be used by other actors and potentially used to execute ransomware.”
SocGholish attack sequences typically begin when users land on compromised websites, where they are prompted to download a fake browser update that, upon execution, triggers the retrieval of additional payloads to the infiltrated machines.
The JavaScript downloader, in this case, activates two disjointed chains, one that leads to the deployment of a fileless variant of AsyncRAT and the other resulting in the BOINC installation.

The BOINC app, which is renamed as “SecurityHealthService.exe” or “trustedinstaller.exe” to evade detection, sets up persistence using a scheduled task by means of a PowerShell script.
The misuse of BOINC for malicious purposes hasn’t gone unnoticed by the project maintainers, who are currently investigating the problem and finding a way to “defeat this malware.” Evidence of the abuse dates back to at least June 26, 2024.
“The motivation and intent of the threat actor by loading this software onto infected hosts isn’t clear at this point,” the researchers said.
“Infected clients actively connecting to malicious BOINC servers present a fairly high risk, as there’s potential for a motivated threat actor to misuse this connection and execute any number of malicious commands or software on the host to further escalate privileges or move laterally through a network and compromise an entire domain.”
The development comes as Check Point said it’s been tracking the use of compiled V8 JavaScript by malware authors to sidestep static detections and conceal remote access trojans, stealers, loaders, cryptocurrency miners, wipers, and ransomware.
“In the ongoing battle between security experts and threat actors, malware developers keep coming up with new tricks to hide their attacks,” security researcher Moshe Marelus said. “It’s not surprising that they’ve started using V8, as this technology is commonly used to create software as it is very widespread and extremely hard to analyze.”