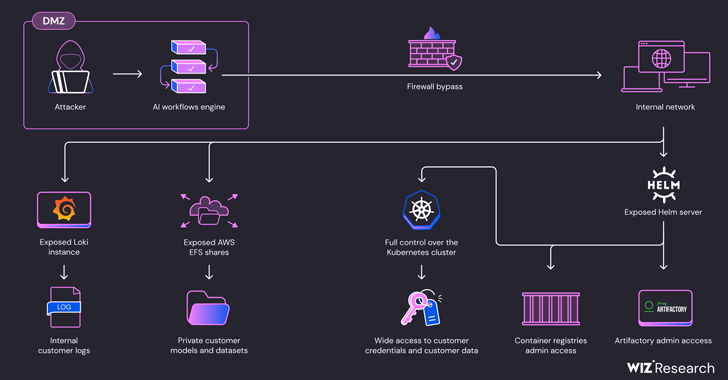
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered security shortcomings in SAP AI Core cloud-based platform for creating and deploying predictive artificial intelligence (AI) workflows that could be exploited to get hold of access tokens and customer data.
The five vulnerabilities have been collectively dubbed SAPwned by cloud security firm Wiz.
“The vulnerabilities we found could have allowed attackers to access customers’ data and contaminate internal artifacts – spreading to related services and other customers’ environments,” security researcher Hillai Ben-Sasson said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
Following responsible disclosure on January 25, 2024, the weaknesses were addressed by SAP as of May 15, 2024.
In a nutshell, the flaws make it possible to obtain unauthorized access to customers’ private artifacts and credentials to cloud environments like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and SAP HANA Cloud.
They could also be used to modify Docker images on SAP’s internal container registry, SAP’s Docker images on the Google Container Registry, and artifacts hosted on SAP’s internal Artifactory server, resulting in a supply chain attack on SAP AI Core services.
Furthermore, the access could be weaponized to gain cluster administrator privileges on SAP AI Core’s Kubernetes cluster by taking advantage of the fact that the Helm package manager server was exposed to both read and write operations.
“Using this access level, an attacker could directly access other customer’s Pods and steal sensitive data, such as models, datasets, and code,” Ben-Sasson explained. “This access also allows attackers to interfere with customer’s Pods, taint AI data and manipulate models’ inference.”
Wiz said the issues arise due to the platform making it feasible to run malicious AI models and training procedures without adequate isolation and sandboxing mechanisms.
“The recent security flaws in AI service providers like Hugging Face, Replicate, and SAP AI Core highlight significant vulnerabilities in their tenant isolation and segmentation implementations,” Ben-Sasson told The Hacker News. “These platforms allow users to run untrusted AI models and training procedures in shared environments, increasing the risk of malicious users being able to access other users’ data.”
“Unlike veteran cloud providers who have vast experience with tenant-isolation practices and use robust isolation techniques like virtual machines, these newer services often lack this knowledge and rely on containerization, which offers weaker security. This underscores the need to raise awareness of the importance of tenant isolation and to push the AI service industry to harden their environments.”
As a result, a threat actor could create a regular AI application on SAP AI Core, bypass network restrictions, and probe the Kubernetes Pod’s internal network to obtain AWS tokens and access customer code and training datasets by exploiting misconfigurations in AWS Elastic File System (EFS) shares.
“People should be aware that AI models are essentially code. When running AI models on your own infrastructure, you could be exposed to potential supply chain attacks,” Ben-Sasson said.
“Only run trusted models from trusted sources, and properly separate between external models and sensitive infrastructure. When using AI services providers, it’s important to verify their tenant-isolation architecture and ensure they apply best practices.”
The findings come as Netskope revealed that the growing enterprise use of generative AI has prompted organizations to use blocking controls, data loss prevention (DLP) tools, real-time coaching, and other mechanisms to mitigate risk.
“Regulated data (data that organizations have a legal duty to protect) makes up more than a third of the sensitive data being shared with generative AI (genAI) applications — presenting a potential risk to businesses of costly data breaches,” the company said.
They also follow the emergence of a new cybercriminal threat group called NullBulge that has trained its sights on AI- and gaming-focused entities since April 2024 with an aim to steal sensitive data and sell compromised OpenAI API keys in underground forums while claiming to be a hacktivist crew “protecting artists around the world” against AI.
“NullBulge targets the software supply chain by weaponizing code in publicly available repositories on GitHub and Hugging Face, leading victims to import malicious libraries, or through mod packs used by gaming and modeling software,” SentinelOne security researcher Jim Walter said.
“The group uses tools like AsyncRAT and XWorm before delivering LockBit payloads built using the leaked LockBit Black builder. Groups like NullBulge represent the ongoing threat of low-barrier-of-entry ransomware, combined with the evergreen effect of info-stealer infections.”