A previously unknown China-linked threat actor dubbed ‘Unfading Sea Haze’ has been targeting military and government entities since 2018.
Bitdefender researchers discovered a previously unknown China-linked threat actor dubbed ‘Unfading Sea Haze’ that has been targeting military and government entities since 2018. The threat group focuses on entities in countries in the South China Sea, experts noticed TTP overlap with operations attributed to APT41.
Bitdefender identified a troubling trend, attackers repeatedly regained access to compromised systems, highlighting vulnerabilities such as poor credential hygiene and inadequate patching practices.
Unfading Sea Haze remained undetected for over five years, despite extensive artifact cross-referencing and public report analysis, no traces of their prior activities were found.
Unfading Sea Haze’s targets confirms an alignment with Chinese interests. The group utilized various variants of the Gh0st RAT, commonly associated with Chinese actors.
A notable technique involved running JScript code through SharpJSHandler, similar to a feature in the “funnyswitch” backdoor linked to APT41. Both methods involve loading .NET assemblies and executing JScript code, suggesting shared coding practices among Chinese threat actors.
However, these findings indicate a sophisticated threat actor possibly connected to the Chinese cyber landscape.
The researchers cannot determine the initial method used by Unfading Sea Haze to infiltrate victim systems because the initial breach happened over six years ago, making hard to recover forensic evidence.
However, the researchers determined that one of methods used by the threat actors to regaining access to the target organizations are spear-phishing emails. The messages use specially crafted archives containing LNK files disguised as regular documents. When clicked, the LNK files would execute malicious commands. The experts observed multiple spear-phishing attempts between March and May 2023.
Some of the email attachment names used in the attacks are:
- SUMMARIZE SPECIAL ORDERS FOR PROMOTIONS CY2023
- Data
- Doc
- Startechup_fINAL
The payload employed in the attacks is a backdoor named SerialPktdoor, however, in March 2024, the researchers observed the threat actors using a new initial access archive files. These archives mimicked the installation process of Microsoft Defender or exploited current US political issues.
The backdoor runs PowerShell scripts and performs operations on files and directories.
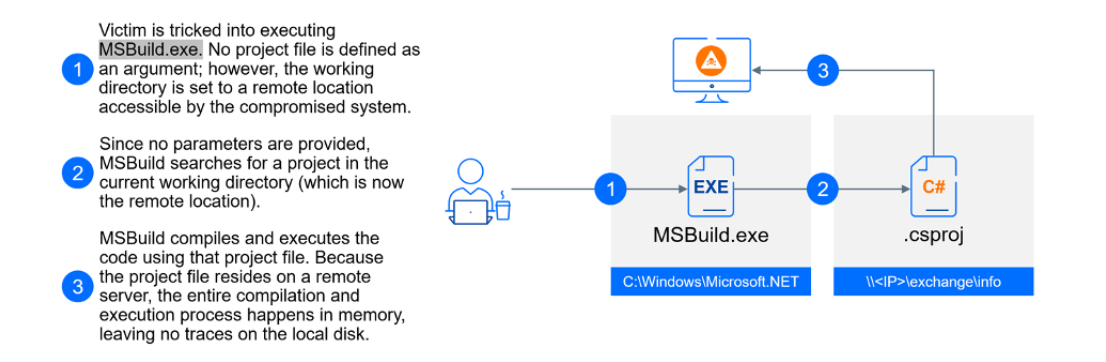
“These LNK files execute a PowerShell command line” reads the report. “This is a clever example of a fileless attack that exploits a legitimate tool: MSBuild.exe. MSBuild, short for Microsoft Build Engine, is a powerful tool for automating the software build process on Windows. MSBuild reads a project file, which specifies the location of all source code components, the order of assembly, and any necessary build tools.”

The threat actors maintain persistence through scheduled tasks, in order to avoid detection attackers used task names impersonating legitimate Windows files. The files are combined with DLL sideloading to execute a malicious payload.
Attackers also manipulate local Administrator accounts to maintain persistence, they were spotted enabling the disabled local Administrator account, followed by resetting its password.
Unfading Sea Haze has notably begun using Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools, particularly ITarian RMM, since at least September 2022 to compromise targets’ networks. This approach represents a significant shift from typical nation-state tactics. Additionally, experts collected evidence that they may have established persistence on web servers, such as Windows IIS and Apache httpd, likely using web shells or malicious modules. However, the exact persistence mechanisms remain unclear due to insufficient forensic data.
The Chinese threat actor has developed a sophisticated collection of custom malware and hacking tools. Since at least 2018, they used SilentGh0st, TranslucentGh0st, and three variants of the .NET agent SharpJSHandler supported by Ps2dllLoader. In 2023, they replaced Ps2dllLoader with a new mechanism using msbuild.exe and C# payloads from a remote SMB share. The attackers also replaced fully featured Gh0stRat variants to more modular, plugin-based versions called FluffyGh0st, InsidiousGh0st (available in C++, C#, and Go), and EtherealGh0st.
“One of the payloads delivered by Ps2dllLoader is SharpJSHandler.” reads the report. “SharpJSHandler operates by listening for HTTP requests. Upon receiving a request, it executes the encoded JavaScript code using the Microsoft.JScript library.
Our investigation also uncovered two additional variations that utilize cloud storage services for communication instead of direct HTTP requests. We have found variations for DropBox and for OneDrive. In this case, SharpJSHandler retrieves the payload periodically from a DropBox/OneDrive account, executes it, and uploads the resulting output back to the same location.
These cloud-based communication methods present a potential challenge for detection as they avoid traditional web shell communication channels.”
The threat actors used both custom malware and off-the-shelf tools to gather sensitive data from victim machines.
One of the malware used for data collection is a keylogger called xkeylog, they also used a web browser data stealer, a tool to monitor the presence of portable devices, and a custom tool named DustyExfilTool.
The attackers are also able to target messaging applications like Telegram and Viber. They first terminate the processes for these apps (telegram.exe and viber.exe), then use rar.exe to archive the application data.
“The Unfading Sea Haze threat actor group has demonstrated a sophisticated approach to cyberattacks. Their custom malware arsenal, including the Gh0st RAT family and Ps2dllLoader, showcases a focus on flexibility and evasion techniques.” concludes the report. “The observed shift towards modularity, dynamic elements, and in-memory execution highlights their efforts to bypass traditional security measures. Attackers are constantly adapting their tactics, necessitating a layered security approach.”