
TL;DR
A low-privileged user on a Linux machine can obtain the root privileges if:
- They can execute
iptablesandiptables-savewithsudoas they can inject a fake/etc/passwdentry in the comment of aniptablesrule and then abusingiptables-saveto overwrite the legitimate/etc/passwdfile. - They can execute
iptableswithsudoand the underlying system misses one of the kernel modules loaded byiptables. In this case they can use the--modprobeargument to run an arbitrary command.
Intro
At some point, some weeks ago, I’ve stumbled upon this fascinating read. In it, the author thoroughly explains an RCE (Remote Code Execution) they found on the Lua interpreter used in the Factorio game. I heartily recommend anyone interested in game scripting, exploit development, or just cool low-level hacks, to check out the blogpost – as it contains a real wealth of insights. The author topped this off by releasing a companion challenge to the writeup; it consists of a Lua interpreter, running Read Full Article ... Fortinet, a major player in the global cybersecurity sector, has disclosed a data breach involving a third-party service, affecting a small number of its Asia-Pacific customers. The breach reportedly exposed limited customer data stored on a cloud-based shared file drive used by Fortinet. However, a hacker, operating under the alias “Fortibitch,” has claimed responsibility for stealing 440 GB of data from the company and leaking it online. Fortinet's operations primarily cater to the enterprise sector, offering endpoint security solutions, firewall management, and cloud security services. With a market valuation of $60 Read Full Article ... Cyber adversary emulation is an assessment method where tactis, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of real-world attackers are used to test the security controls of a system. It helps to understand how an attacker might penetrate defenses, to evaluate installed security mechanisms and to improve the security posture by addressing identified weaknesses. Furthermore, it allows running training scenarios for security professionals, e.g., in cyber ranges where practical exercises can be performed. Unfortunately, adversary emulation requires significant time, effort, and specialized professionals to conduct.
During a distributed denial-of-service campaign targeting organizations in the financial services, internet, and telecommunications sectors, volumetric attacks peaked at 3.8 terabits per second, the largest publicly recorded to date. The assault consisted of a “month-long” barrage of more than 100 hyper-volumetric DDoS attacks flooding the network infrastructure with garbage data. In a volumetric DDoS attack, the target is overwhelmed with large amounts of data to the point that they consume the bandwidth or exhaust the resources of applications and devices, leaving legitimate users with no access.
In a revealing new study, cybersecurity researchers from Germany have highlighted significant vulnerabilities and operational challenges within the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) protocol, raising serious concerns about its current stability and security. While the protocol was designed to bolster the safety of internet traffic routing, researchers suggest it may fall short of its promises. RPKI was introduced as a remedy for the inherent flaws in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), the backbone of internet traffic routing, which lacked essential security measures. RPKI enhances security by enabling network operators to verify Read Full Article ... A high-severity vulnerability (CVE-2024-5102) has been discovered in Avast Antivirus for Windows, potentially allowing attackers to gain elevated privileges and wreak havoc on users’ systems. This flaw, present in versions prior to 24.2, resides within the “Repair” feature, a tool designed to fix issues with the antivirus software itself. The vulnerability stems from how the repair function handles symbolic links (symlinks). By manipulating these links, an attacker can trick the repair function into deleting arbitrary files or even executing code with the highest system privileges (NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM). This could allow them Read Full Article ... Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up and Using the Custom Search API in Google Colab Have you ever wished for a more personalized search engine that caters exclusively to your preferences and trusted sources? In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to create your own custom search engine using Google’s Programmable Search Engine and call the Custom Search API in Google Colab using Python. Say hello to your very own, tailored Google! Who’s doing what? Different parts of the security community have different perspectives on Rogue AI: FortiGuard Labs gathers data on ransomware variants of interest that have been gaining traction within our datasets and the OSINT community. The Ransomware Roundup report aims to provide readers with brief insights into the evolving ransomware landscape and the Fortinet solutions that protect against those variants. This edition of the Ransomware Roundup covers the Underground ransomware. Affected platforms: Microsoft Windows
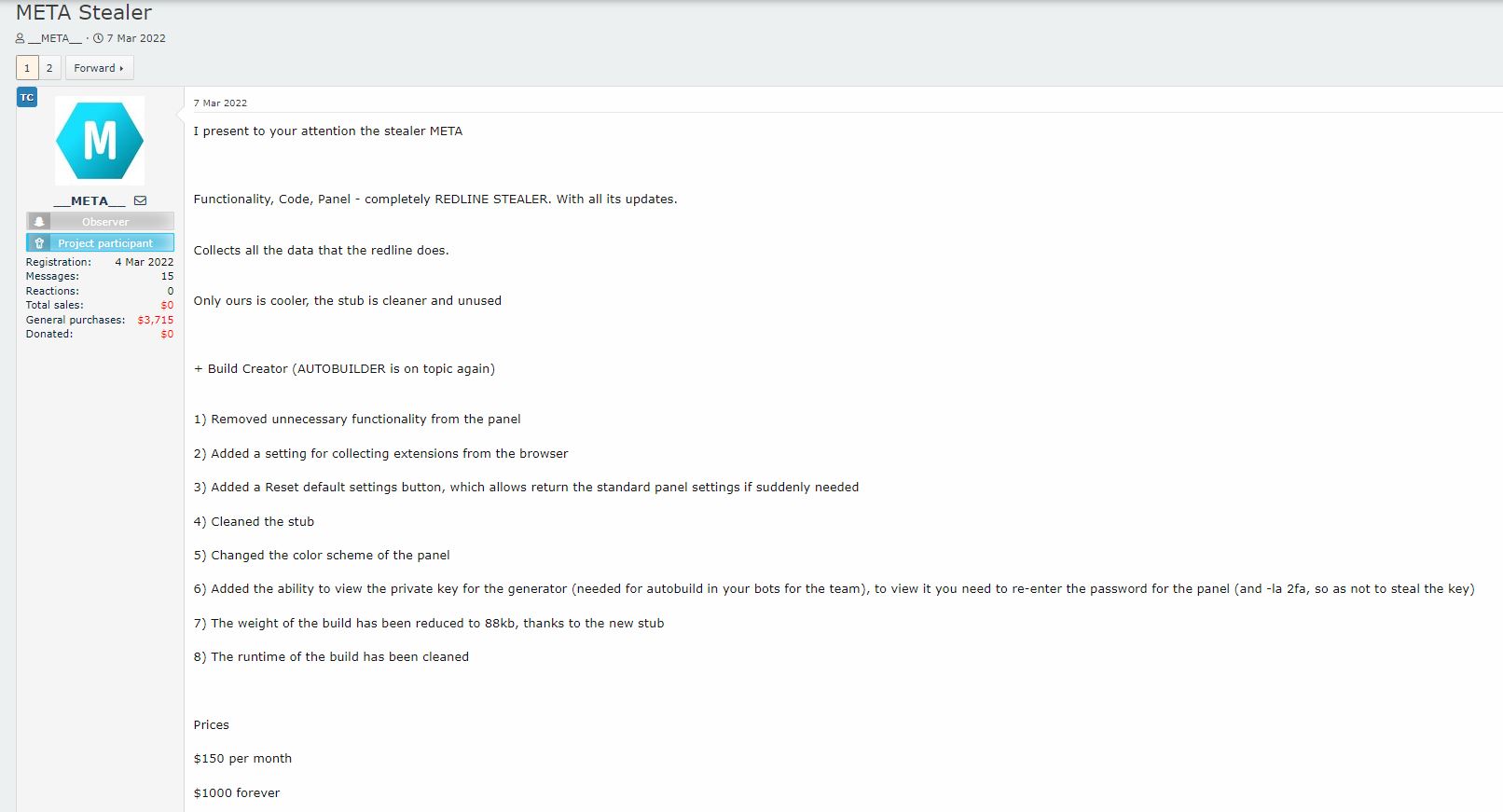
Affected Platforms: Microsoft Windows In August 2024, FortiGuard Labs observed a python infostealer we call Emansrepo that is distributed via emails that include fake purchase orders and invoices. Emansrepo compresses data from the victim’s browsers and files in specific paths into a zip file and sends it to the attacker’s email. According to our research, this campaign has been ongoing since November 2023. The attacker sent a phishing mail containing an HTML Read Full Article ... Affected Platforms: GeoServer prior to versions 2.23.6, 2.24.4, and 2.25.2 GeoServer is an open-source software server written in Java that allows users to share and edit geospatial data. It is the reference implementation of the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Web Feature Service (WFS) and Web Coverage Service (WCS) standards. On July 1, the project maintainers released an advisory for the vulnerability CVE-2024-36401 (CVSS score: 9.8). Multiple OGC request parameters allow remote code execution Read Full Article ... How does Pegasus and other spyware work discreetly to access everything on your iOS device? In today’s digital age, mobile phones and devices have evolved from being exclusive to a few to becoming an absolute need for everyone, aiding us in both personal and professional pursuits. However, these devices, often considered personal, can compromise our privacy when accessed by nefarious cybercriminals. Malicious mobile software has time and again been wielded as a sneaky weapon to compromise the sensitive information of targeted individuals. Cybercriminals build Read Full Article ... In the recent Hi-Tech Crime Trends report, Group-IB experts highlighted a concerning shift in the focus of cybercriminals towards Apple devices. The shift is driven by the increasing popularity and adoption of Apple products in both consumer and corporate environments. As a result, the number of malicious programs targeting iOS and macOS devices has risen exponentially. The App Store, once considered highly secure, is now at risk of frequent attempts to distribute malware. The increased use of iCloud and other Apple cloud services Read Full Article ... In May 2024, the Group-IB team received a request from a Malaysia-based financial organization to investigate a malware sample targeting its clients in the Asia-Pacific region. Based on details from the customer and the analysis by the Group-IB Fraud Protection team, the malware scenario was reconstructed as follows: The victim visited a phishing website impersonating a local legitimate food brand, which prompted the victim to download an app to make a purchase. Approximately 5 minutes after downloading the app, Read Full Article ... In January 2024, during the analysis of the infrastructure used by ShadowSyndicate Group-IB Threat Intelligence analysts detected a landing page designed to distribute the BMANAGER modular trojan, created by threat actor dubbed Boolka. Further analysis revealed that this landing page served as a test run for a malware delivery platform based on BeEF framework. The threat actor behind this campaign has been carrying out opportunistic SQL injection attacks against websites in various countries since at least 2022. Over the last three years, the threat actor have been infecting vulnerable websites Read Full Article ... Discovered by Group-IB in May 2024, the Ajina.Banker malware is a major cyber threat in the Central Asia region, disguising itself as legitimate apps to steal banking information and intercept 2FA messages. In May 2024, Group-IB analysts discovered suspicious activity targeting bank customers in the Central Asia region. The threat actors have been spreading malicious Android malware designed to steal users’ personal and banking information, and potentially intercept 2FA messages. During the investigation, Group-IB discovered .APK files masquerading as legitimate applications that facilitated payments, banking, Read Full Article ... SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a core component of the internet's email infrastructure, responsible for sending and receiving emails. It's a protocol within the TCP/IP suite, frequently working alongside POP3 or IMAP to store emails on servers and allow users to access them. Despite its widespread use, SMTP has certain vulnerabilities that make it a popular target for penetration testers and hackers. HELO It’s the first SMTP command: is starts the conversation identifying the sender server and is generally Read Full Article ... Potentially allowing an attacker to read certain information on Check Point Security Gateways once connected to the internet and enabled with Remote Access VPN or Mobile Access Software Blades. A security fix that mitigates this vulnerability is available. Read about it — CVE-2024-4956 Disclaimer: This Proof of Concept (POC) is made Read Full Article ... CVE-2024-23692 is a critical vulnerability in Rejetto HTTP File Server (HFS) version 2.3m, allowing unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE). This flaw enables attackers to execute arbitrary code on the server, posing significant security risks. In this post, we examine Rejetto HFS, the affected versions, the impact of the vulnerability, and the timeline of its discovery and remediation. CVE-2024-23897 is a critical vulnerability in Jenkins that allows unauthenticated attackers to read arbitrary files on the Jenkins controller's file system. This flaw arises from improper handling of command arguments in the args4j library, specifically in command-line operations where an @ character followed by a file path can lead to unauthorized file content exposure. This vulnerability poses a significant risk as it can enable attackers to access sensitive information, such as cryptographic keys and configuration files, which may be leveraged for Read Full Article ... Misconfigurations are often the weakest link in an otherwise secure environment. One of the most dangerous yet easily overlooked misconfigurations in Django is leaving In Django, the This post is part of an analysis that I have carried out during my spare time, motivated by a friend that asked me to have a look at the DDosia project related to the NoName057(16) group. The reason behind this request was caused by DDosia client changes for performing the DDos attacks. Because of that, all procedures used so far for monitoring NoName057(16) activities did not work anymore. Before starting to reverse DDosia Windows sample, I preferred to gather as much information Read Full Article ... Because of the massive Ursnif campaigns that hit Italy during the last weeks, I was looking for a lightweight method to quickly extract the last infection stage of all collected samples, in order to start further analysis effectively. Due to this, I wrote a little frida script that performs basic Dynamic Binary Instrumentation (DBI) to monitor useful function calls and extracts the Ursnif payload. In this article I am going to briefly discuss this script and the steps needed to start analyzing the resulting binary. Meduza Stealer … Yes, you read it right, I did not misspelled it, is a new stealer that appeared on Russian-speaking forums at the beginning of June 2023. The stealer is written in C++ and is approximately 600KB in size. The DLL dependencies are statically linked to the binary, which reduces the detection. It’s also worth noting that the collected logs are not stored on the disk. WhiteSnake Stealer first appeared on hacking forums at the beginning of February 2022. The stealer collects data from various browsers such as Firefox, Chrome, Chromium, Edge, Brave, Vivaldi, CocCoc, and CentBrowser. Besides browsing data, it also collects data from Thunderbird, OBS-Studio, FileZilla, Snowflake-SSH, Steam, Signal, Telegram, Discord, Pidgin, Authy, WinAuth, Outlook, Foxmail, The Bat!, CoreFTP, WinSCP, AzireVPN, WindscribeVPN. The following are Read Full Article ... MetaStealer made its debut on Russian hacking forums on March 7, 2022. The stealer is said to incorporate the functionality, code, and panel of Redline Stealer. The developer claims to have improved the stub of the payload. It is priced at $150 per month, mirroring the price of Redline Stealer. Note: Some samples of MetaStealer have been found in sandbox platforms like Triage, Joe Sandbox, Any.run and classified Read Full Article ... Pure Logs Stealer first appeared on hacking forums at the end of October 2022. The stealer is developed by a malware developer going under the alias PureCoder. The malware developer is also behind in developing the products shown above, such as Pure Miner, Pure Crypter, Pure hVNC, Blue Loader, and other products, including HWID Read Full Article ... Previously, I wrote a blog going through some of MetaStealer’s functionalities and did a brief comparison with Redline since they are both very similar but, at the same time, different. You might say that all stealers are the same because they have one purpose - to steal. However, each of them is somewhat different from the others, even if they borrowed the code from their predecessors. Every stealer tries to be better than the other one despite having Read Full Article ... Atomic Stealer is known to be the first stealer for MacOS devices, it first appeared on Russian hacking in March, 2023. For 3000$ per month, the user gets the access to the panel. The user provides Telegram Bot ID and build ID to the seller and the user receives the build. The stealer allegedly has the following functionalities and features:
AlcaWASM Challenge Writeup – Pwning an In-Browser Lua Interpreter

Introduction
Fortinet Confirms Third-Party Data Breach Amid Hacker’s 440 GB Theft Claim

Adversary Emulation is a Complicated Profession – Intelligent Cyber Adversary Emulation with the Bounty Hunter

Cyber Adversary Emulation
Cloudflare blocks largest recorded DDoS attack peaking at 3.8Tbps

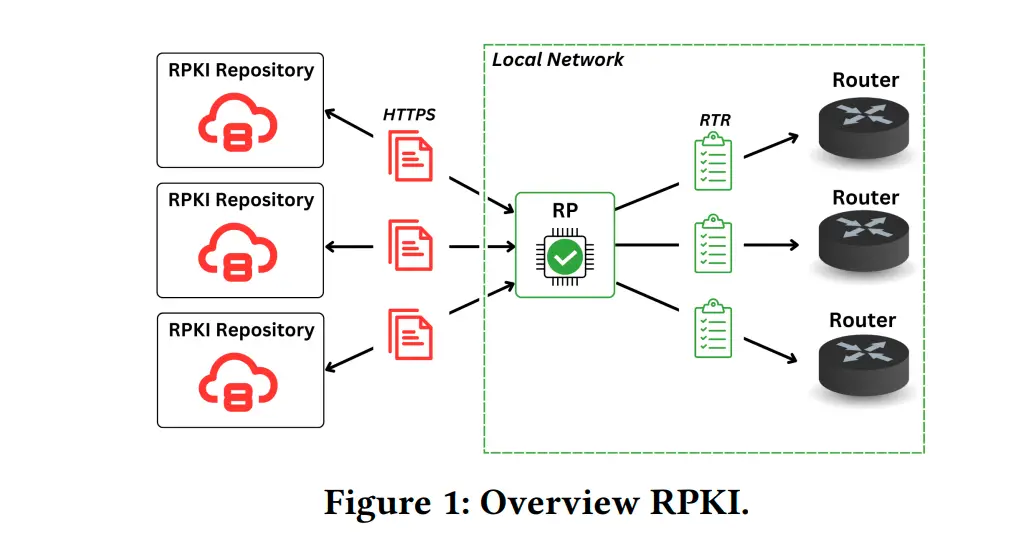
RPKI Security Under Fire: 53 Vulnerabilities Exposed in New Research
CVE-2024-5102: Avast Antivirus Flaw Could Allow Hackers to Delete Files and Run Code as SYSTEM

Build Your Own Google: Create a Custom Search Engine with Trusted Sources

Introduction:
Read Full Article ...
Rogue AI: What the Security Community is Missing

Ransomware Roundup – Underground

Impacted parties: Microsoft Windows
Impact: Encrypts victims' files and demands ransom for file decryption
Severity level: HighUnderground Ransomware Overview
Emansrepo Stealer: Multi-Vector Attack Chains

Impacted Users: Microsoft Windows
Impact: The stolen information can be used for future attack
Severity Level: HighThreat Actors Exploit GeoServer Vulnerability CVE-2024-36401

Impacted Users: Any organization
Impact: Remote attackers gain control of the vulnerable systems
Severity Level: CriticalIn-depth analysis of Pegasus spyware and how to detect it on your iOS device

IntroductionGoldPickaxe exposed: How Group-IB analyzed the face-stealing iOS Trojan and how to do it yourself

Introduction
Beware CraxsRAT: Android Remote Access malware strikes in Malaysia

Background
Boolka Unveiled: From web attacks to modular malware
Introduction
Ajina attacks Central Asia: Story of an Uzbek Android Pandemic

Introduction
SMTP/s — Port 25,465,587 For Pentesters

SMTP Commands:
POC – CVE-2024–4956 – Nexus Repository Manager 3 Unauthenticated Path Traversal

CVE-2024-4956
POC - CVE-2024–4956 - Nexus Repository Manager 3 Unauthenticated Path Traversal
Unauthenticated RCE Flaw in Rejetto HTTP File Server – CVE-2024-23692

POC - Unauthenticated RCE Flaw in Rejetto HTTP File Server - CVE-2024-2369
Overview
CVE-2024–23897 — Jenkins File Read Vulnerability — POC

Basic info
Why Django’s [DEBUG=True] is a Goldmine for Hackers
DEBUG=True in a production environment. From an attacker’s perspective, this is a goldmine for reconnaissance and exploitation. This article explores how attackers can exploit this setting and the top five valuable data types they can retrieve from a vulnerable Django application.What Does DEBUG=True Do in Django?
DEBUG setting controls whether debug information, including error stack traces Read Full Article ...Extracting DDosia targets from process memory

Introduction
Dynamic Binary Instrumentation for Malware Analysis

Introduction
Meduza Stealer or The Return of The Infamous Aurora Stealer

Meduza’s Gaze
Unleashing the Viper : A Technical Analysis of WhiteSnake Stealer

Case Study

MetaStealer – Redline’s Doppelgänger

Case Study
Pure Logs Stealer Fails to Impress

Case Study


MetaStealer Part 2, Google Cookie Refresher Madness and Stealer Drama

Stealer’s World of Drama
From Russia With Code: Disarming Atomic Stealer

Case Study
